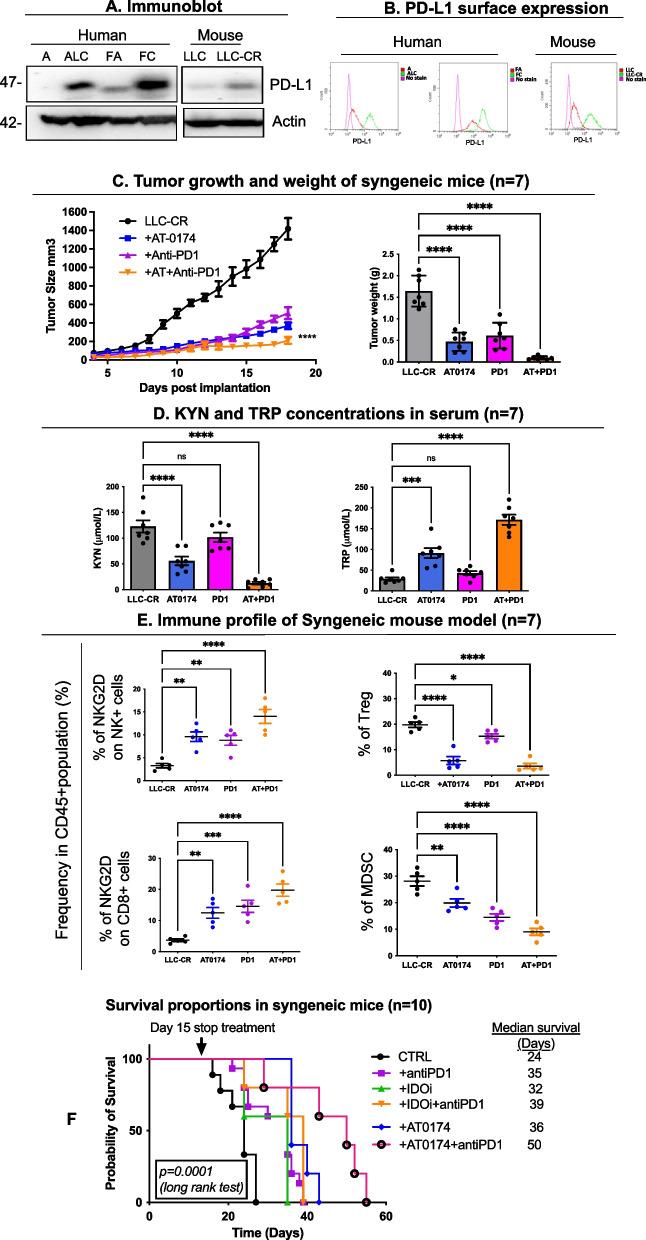
Fig. 6.
Antitumor efficacy of PD-1 blockage is further enhanced by IDO1/TDO2 inhibition. A Immunoblot of PD-L1 in CS vs. CR cells in human and mouse cell lines. B Flow cytometry of surface PD-L1 in CS vs. CR cells. CR cells exhibited significantly higher PD-L1 expression. C Antitumor efficacy of AT-0174 plus anti-PD-1 antibody in syngeneic mice bearing LLC-CR. Tumor size and weight were significantly decreased upon dual inhibition plus anti-PD-1 treatment. D KYN concentrations were significantly reduced and TRP concentrations were significantly higher in mice treated with AT-0174 compared to the control. This result was maintained and further heightened by combining AT-0174 and anti-PD-1 antibody. E Flow cytometry characterization of immune profile in tumors. Decreased T-reg populations were found in both single and combination treatments in syngeneic mice bearing LLC-CR. AT-0174 enhanced NKG2D frequencies on NK and CD8 + T cell populations. Significant decreases in MDSC populations were found in combination treatments. F Kaplan–Meier survival curves for the in vivo assessment of AT-0174 alone, IDOi alone, and combination treatment with anti-PD-1 antibodies were assessed in the syngeneic mouse model. Since tumor size was significantly reduced, treatments were stopped on day 15, and efficacy was determined by comparing the median times to the endpoint (either death or euthanasia for advanced tumor progression). Data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons for tumor growth and Dunnett’s multiple comparisons for the tumor weight, immune profile, and KYN/TRP concentrations with *P < 0.05, **P < 0.005, ***P < 0.0005, ****P < 0.0001