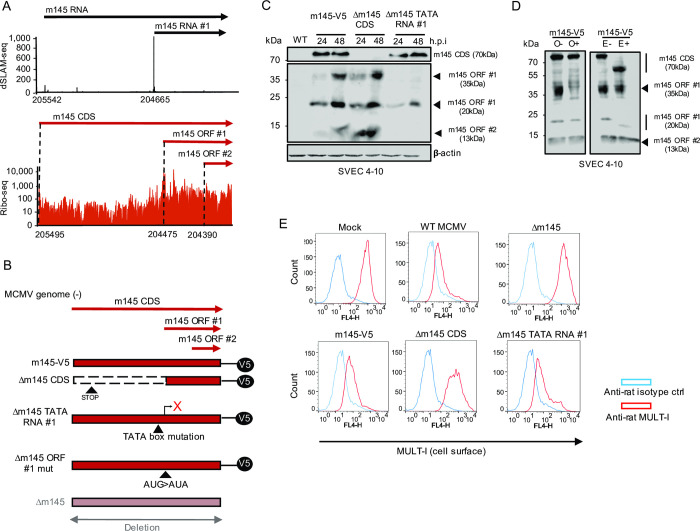
Fig 8. Characterization of N-terminally truncated ORFs in the m145 locus.
A. ORFs and transcripts expressed from the m145 locus. This includes the so far unknown m145 ORF #1 and #2 expressed from m145 RNA #1. Coordinates for the TiSS and ORF start codon are shown for each transcript and ORF. dSLAM-seq data are shown in linear scale, Ribo-seq data in logarithmic scale. Aggregated reads across all time points mapping to the m145 locus are shown. B. Schematic representation of the MCMV mutants generated to characterize novel viral gene products encoded by the m145 locus. Mutant viruses were generated based on a reporter virus with a V5-tag inserted at the C-terminus of the canonical m145 CDS. The viruses were generated by en passant BAC mutagenesis as described in methods on this backbone. The Δm145 CDS harbored a STOP codon at the 40th codon to skip additional AUGs downstream of the m145 CDS signal peptide which may have resulted in additional products, hindering accurate analysis of the locus. The Δm145 TATA RNA #1 mutant included a mutation in the TATA box of the respective transcript to abrogate gene expression downstream while the Δm145 ORF #1 mut mutant was created by mutating the start codon of m145 ORF #1. The Δm145 virus is a previously created virus where the entire m145 locus (i.e. m145 CDS) was replaced by a kanamycin cassette. C. SVEC 4–10 murine endothelial cells were infected with the indicated viruses at an MOI of 1 for 24 and 48 h. V5-tagged m145 gene products were characterized by Western blot. Parental WT MCMV infection was used as negative control. D. SVEC 4–10 cells were infected for 48 h with the m145-V5 virus at an MOI of 1. Cells were harvested and treated with or without EndoHf (E) or O-glycosidase (O) to qualitatively analyze glycosylation patterns of m145 gene products via Western blot. The m145 CDS gene product of 70 kDa shifted to 55 kDa upon EndoHf treatment justifying its actual predicted weight. E. SVEC 4–10 cells were infected with m145 virus mutants at an MOI of 1 for 18 h and stained with rat anti-MULT-I and mouse anti-m04 antibodies following cell surface MULT-I analysis through flow cytometry by gating on infected cells (m04+). Anti-rat and anti-mouse isotype antibodies were utilized as negative controls. Western blots and flow cytometry histograms are a representative for two (n = 2) and three biological replicates (n = 3), respectively.