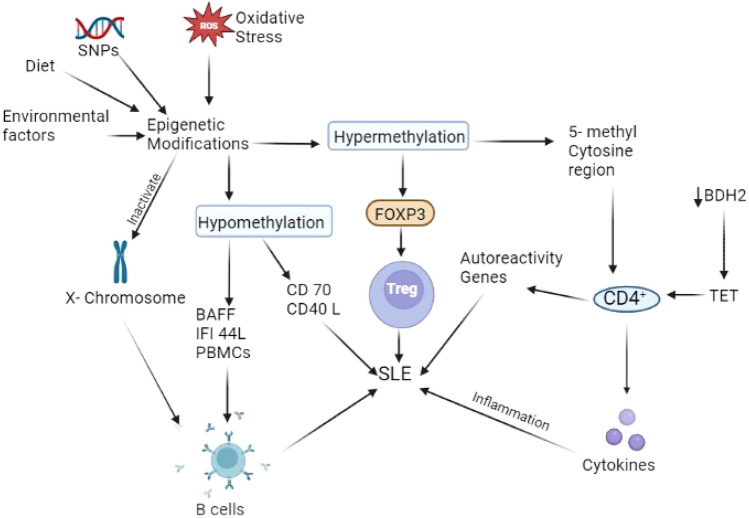
Fig. 4.
Epigenetics implications modifies the various mechanisms involved in lupus pathology. Oxidative stress and diet have been recently shown as the important triggers of the epigenetic events demonstrates the importance of environmental factors in disease etiology. Methylation patterns have been found potentially involved in modulation of immunobiology via regulating the T reg and B cell activity. Hypermethylation of the anti-inflammatory sites and hypomethylation of pro-inflammatory genes have been demonstrated in recent studies. Epigenetic events can potentially modulate the lupus outcomes and can be utilized for diagnosis as biomarkers. SNP single-nucleotide polymorphism, BAFF B-cell activating factor, IFI 44L Interferon-inducible 44 like, PBMC Peripheral blood mononuclear cells, FOXP3 forkhead box P3, BDH2 3-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase 2, TET ten–eleven translocation, ROS reactive oxygen species