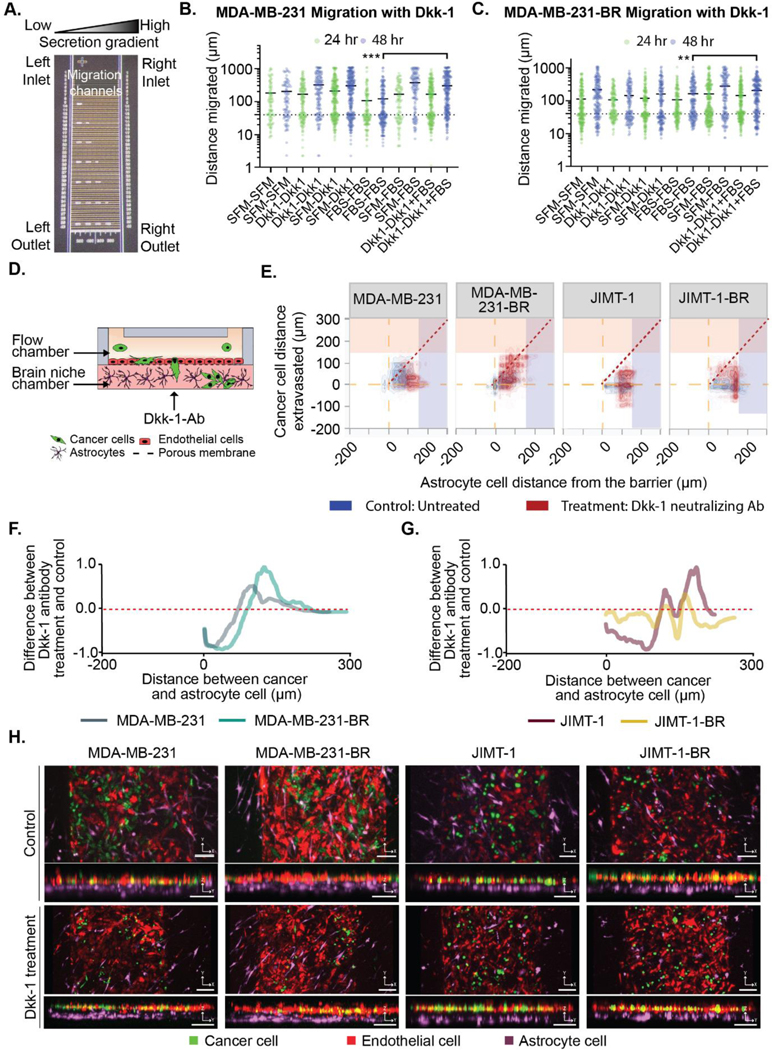
Figure 5. The Dkk-1 cytokine influences cancer cell extravasation and interaction with astrocytes.
(A-B) Purified Dkk-1 was tested as a chemoattractant/stimulant for cancer cell migration using microfluidic device. (A) Image of the microfluidic migration chip. Details in the supplemental methods. (B) MDA-MB-231 and (C) MDA-MB-231-BR cell migration in chemotactic gradients using combinations of: serum free media (SFM), FBS and 20 ng/mL Dkk-1. (D-H) Cancer cells in BBN chips with astrocytes treated with or without Dkk-1 neutralization antibody (10 μg/mL) for MDA-MB-231, MDA-MB-231-BR, JIMT-1, JIMT-1-BR. (D) Dkk-1 neutralizing antibody was administered in the brain niche chamber. (E) Distance (μm) between the cancer cells and the endothelial barrier in BBN chips compared to astrocyte cell position treated with or without Dkk-1 neutralization antibody (10 μg/mL) for MDA-MB-231, MDA-MB-231-BR, JIMT-1, JIMT-1-BR. (F-G) Difference between the samples treated with Dkk-1 neutralizing Ab and untreated samples for (F) MDA-MB-231-BR and MDA-MB-231 cells, and (G) JIMT-1-BR or JIMT-1. (H) Confocal images of cancer cell extravasation into BBN chips treated with 10 μg/mL Dkk-1 neutralization antibody, scale bar 125 μm. (B-C) **p < 6.25*10−3, ***p < 6.25*10−4, Mann-Whitney significance tests with a Bonferroni correction. A-B was performed with three biolgoical replicates each with three technical replicates,refer to Table S1 for list of replicates per condition in D-H.