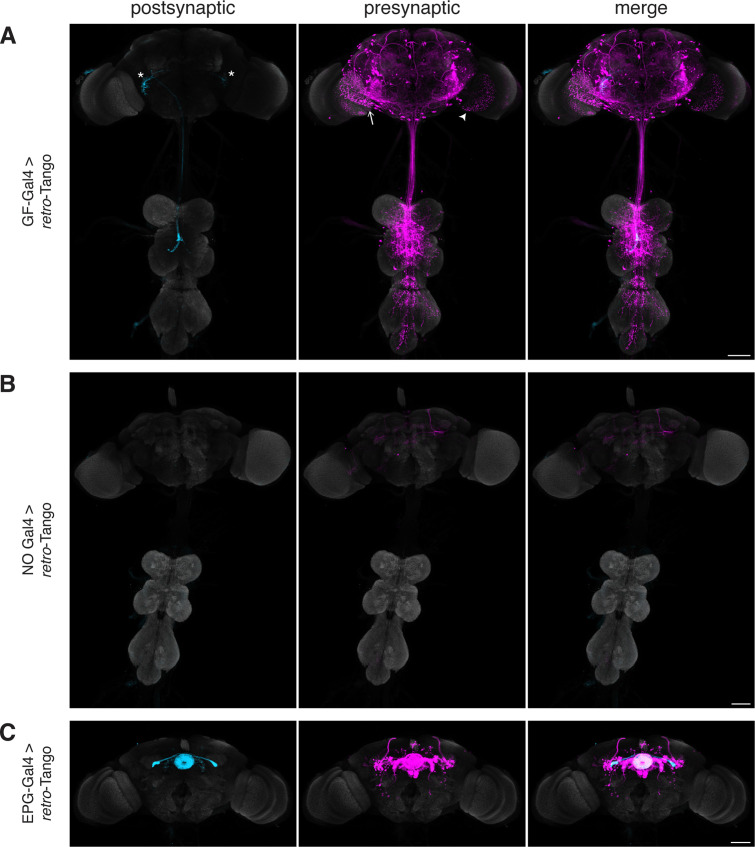
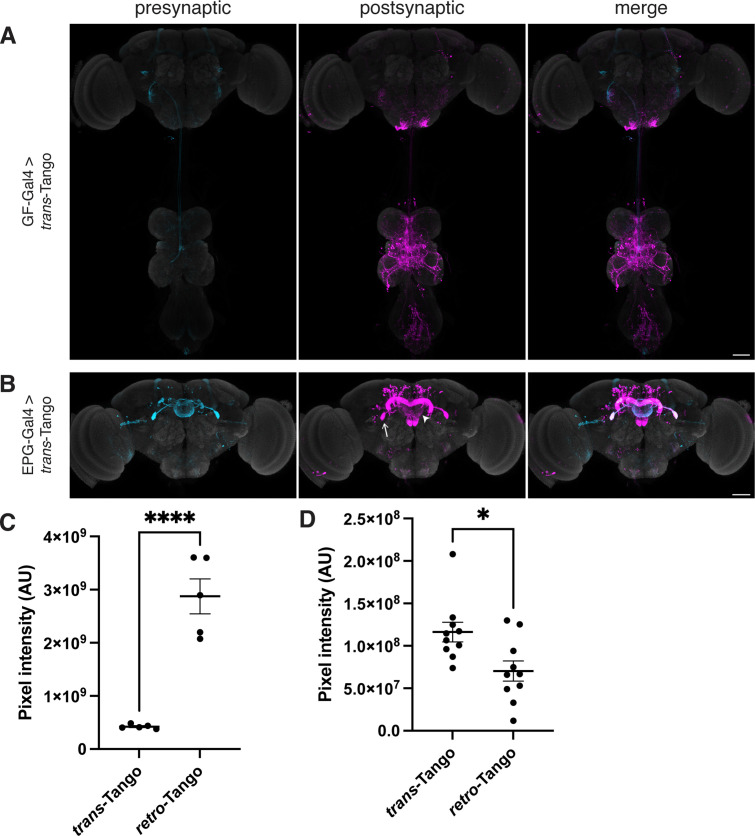
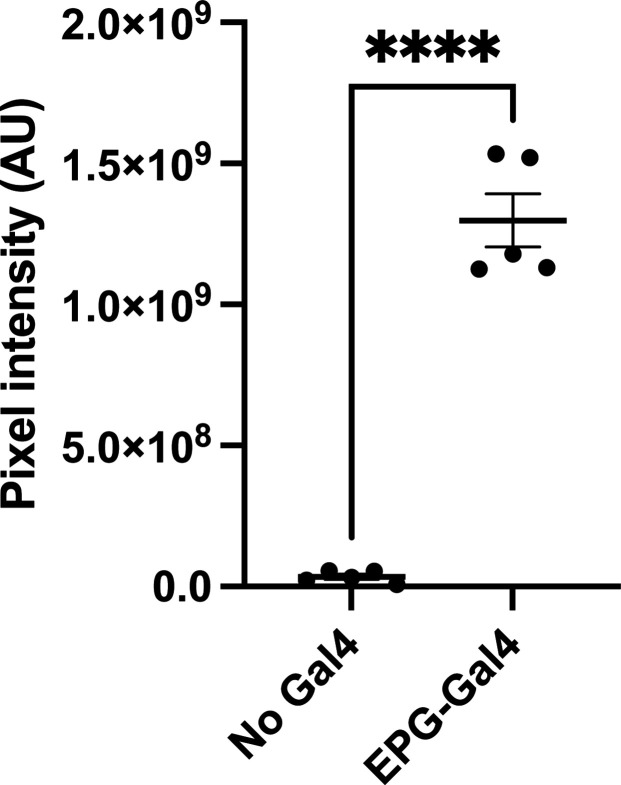
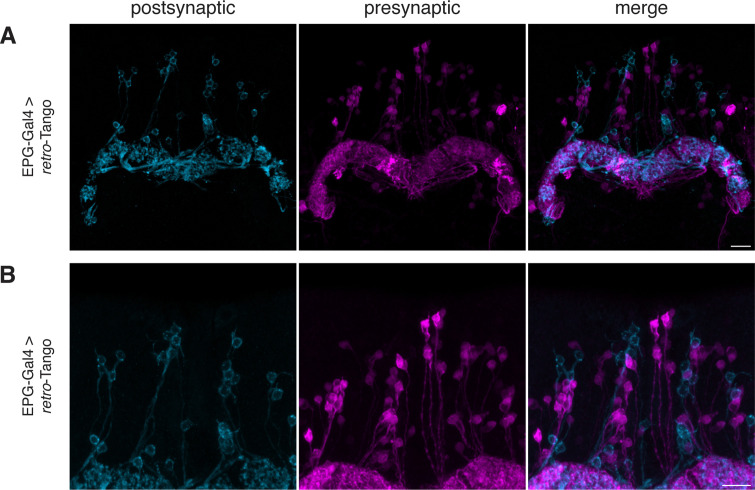
Figure 2. Implementation of retro-Tango in the giant fiber and central complex circuits.
(A) Initiating retro-Tango from the GFs (asterisks mark the cell bodies) results in presynaptic signal in the brain and VNC (223±59 neurons in 5 brains, 1±3 neurons in 5 VNCs). Both LC4 (arrow) and LPLC2 (arrowhead) neurons, known presynaptic partners of GFs, are identified by retro-Tango. Note the asymmetry between hemispheres in the signal in the postsynaptic starter neurons and their corresponding presynaptic partners. (B) retro-Tango exhibits little background noise in the absence of a Gal4 driver. Background is observed in the mushroom bodies, in the central complex, and in a few neurons in the VNC (68±10 neurons in 4 brains, 1±1 neurons in 4 VNCs). (C) Ligand expression in EPG neurons of the central complex leads to retro-Tango signal in their known presynaptic partners: PEN, PFR and Δ7 neurons (170±24 neurons in 5 brains). The signal in these neurons can be easily discerned from the background noise. 15do males were analyzed for all panels. Postsynaptic GFP (cyan), presynaptic mtdTomato (magenta) and neuropil (grey). Scale bars, 50 μm.