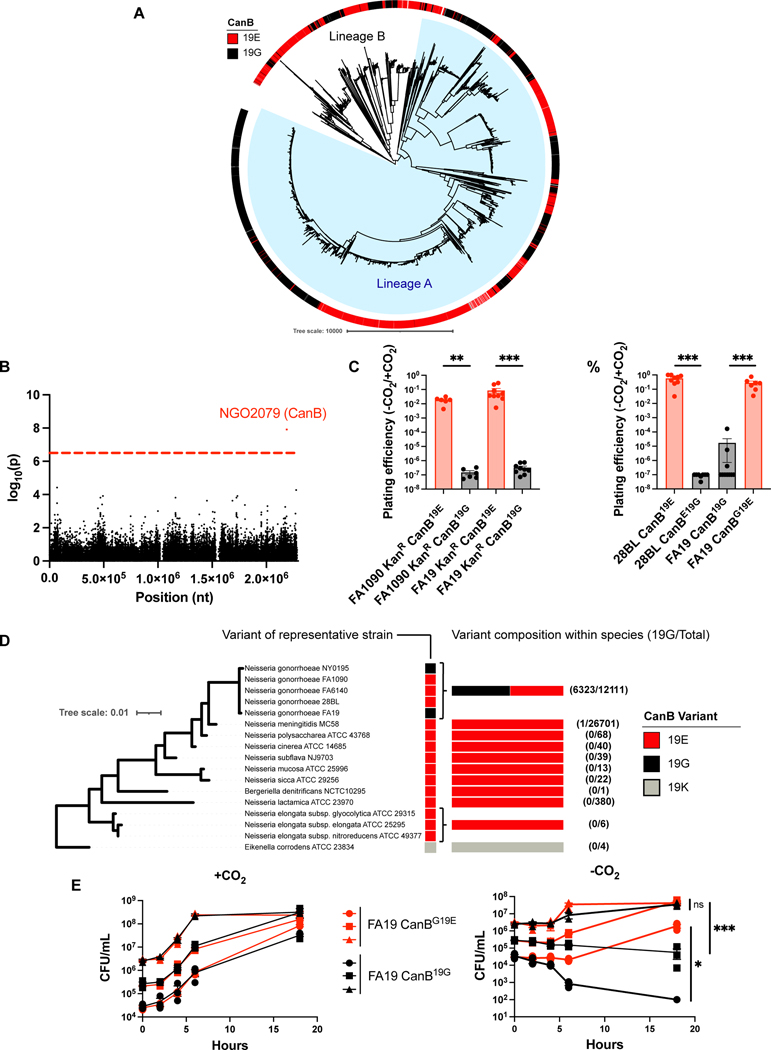
Figure 1.
A SNP in ngo2079, encoding a β-carbonic anhydrase, is necessary and sufficient to explain dependence on supplemental CO2 in N. gonorrhoeae. (A) Maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree of 5,007 strains of N. gonorrhoeae with a colored track representing CanB variant. Branch length represents total number of substitutions after removal of predicted recombinations. Lineage A represents isolates that arose phylogeographically After the introduction of N. gonorrhoeae into Asia, while Lineage B represents isolates that arose Before that breakpoint, as defined by Sánchez-Busó et al.12 (B) Manhattan plot of SNPs associated with dependence on supplemental CO2 across 30 strains of N. gonorrhoeae. Dotted line represents a p-value of 0.05 with Bonferroni correction for 57,691 unitigs. (C) Plating efficiencies in the absence and presence of 5% supplemental CO2 of CanB variants introduced by kanamycin co-selection in N. gonorrhoeae strains FA1090 (parental CanB19E) and FA19 (parental CanB19G) (From left to right, N = 6, 6, 9, 9, from two independent experiments, error bars represent SEM). Significance (from left to right, p = 0.00512, p = 0.00062) determined by two-sided Mann-Whitney U test. (D) Plating efficiencies as in (C) of N. gonorrhoeae strains 28BL (parental CanB19E) and FA19 (parental CanB19G) with isogenic CanB mutants (from left to right, N = 9, 8, 10, 7, from two independent experiments, error bars represent SEM). Significance (from left to right, p = 0.00062, p = 0.00076) determined by two-sided Mann-Whitney U test. (E) NGO2079/CanB variants across sequenced Neisseria and related species represented alongside a 16S maximum-likelihood tree. Branch length represents number of substitutions per site. (F) Growth of FA19 CanB isogenic strains in the presence and absence of supplemental CO2 (N=3, representative of two independent experiments, error bars represent SEM). Significance (from top to bottom, p = 0.45, p = 0.00069, p = 0.014) at 18 hours determined by unpaired two-sided t-test. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, 599 ***p<0.001