Figure 8.
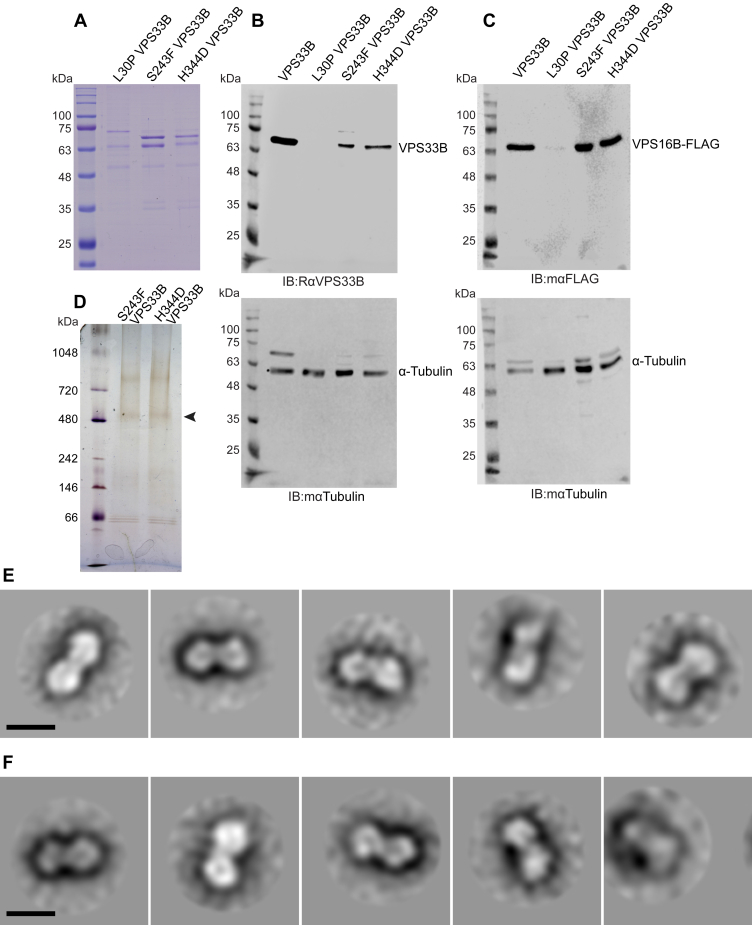
Effects of ARC-syndrome causative VPS33B variants L30P, S243F, and H344D on complex formation.A, SDS-PAGE gel of complexes containing VPS33B L30P, S243F, and H344D purified from yeast shows VPS33B is mostly absent in the L30P sample and VPS16B is also reduced. B, immunoblotting for VPS33B in yeast lysates expressing VPS33B wildtype, L30P, S243F, and H344D along with wildtype VPS16B-3xFLAG show VPS33B is undetectable in the L30P lysate. C, immunoblotting for VPS16B-3xFLAG in yeast lysates from cultures expressing VPS33B wildtype, L30P, S243F, and H344D shows FLAG signal is weak in the L30P lysate. For (B) and (C), nitrocellulose membranes were blotted for α-tubulin as loading control without stripping. D, silver-stained BN-PAGE gel of complexes containing VPS33B S243F or H344D showing that these variants do not disrupt complex formation. Complex indicated by arrowhead. E, 2D class averages from negative-staining EM of VPS33B–VPS16B-3xFLAG complexes containing VPS33B S243F mutation. Classes generated from 257 particles. The scale bar represents 10 nm. F, 2D class averages from negative-staining EM of VPS33B–VPS16B-3xFLAG complexes containing VPS33B H344D mutation. Classes generated from 259 particles. The scale bar represents 10 nm. ARC, arthrogryposis, renal dysfunction, and cholestasis; BN-PAGE, blue native polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis; VPS, vacuolar protein sorting protein.