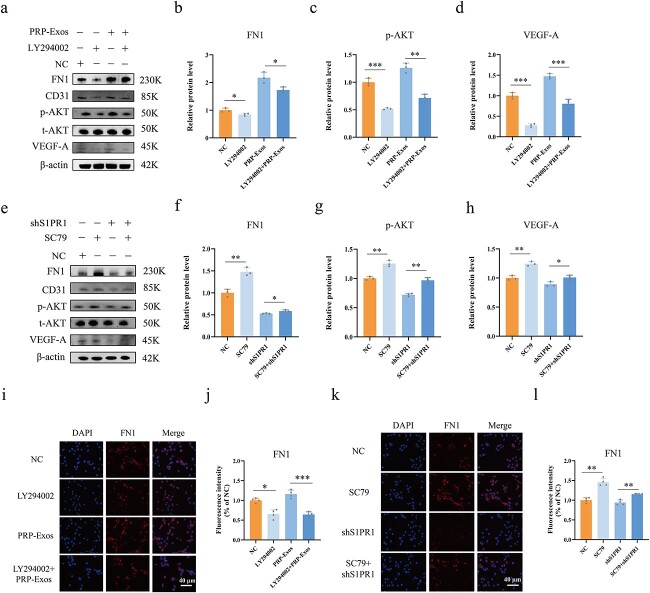
Figure 7.
PRP-Exos-S1P regulates FN1 via the AKT signalling pathway. (a–d) The relative levels of FN1, p-AKT and VEGF-A in HUVECs after different treatments were measured by western blotting in the LY294002 vs NC and LY294002 + PRP-Exos vs PRP-Exos groups. (e–h) The relative levels of FN1, p-AKT and VEGF-A in HUVECs after different treatments were measured by western blotting in the SC79 vs NC and SC79 + shS1PR1 vs shS1PR1 groups. (i, j) Immunofluorescence for FN1 was measured in the LY294002 vs NC and LY294002 + PRP-Exos vs PRP-Exos groups. (k, l) Immunofluorescence for FN1 was measured in the SC79 vs NC and SC79 + shS1PR1 vs shS1PR1 groups. ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05. LY294002 inhibitor of AKT phosphorylation, SC79 agonist of AKT phosphorylation, NC normal control, PRP platelet-rich plasm, PRPExos exosomes derived from PRP, FN1 fibronectin 1, p-AKT phosphorylated protein kinase B, t-AKT total protein kinase B, VEGF-A vascular endothelial growth factor A