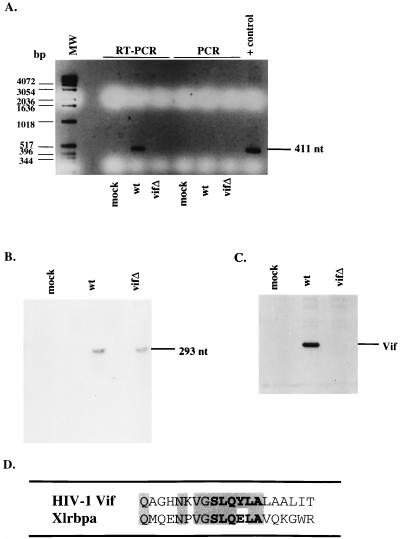
FIG. 5.
Association of Vif with viral genomic RNA. (A) H9 cell lysates from mock-infected cells or cells expressing the wild type (wt) or vif mutant (vifΔ) were subjected to immunoprecipitation with antiserum against Vif. Immunoprecipitated pellets were either directly PCR amplified with primers directed against the HIV-1 genome, or cDNA synthesis was performed first with avian myeloblastosis virus RT, followed by PCR. Direct PCR amplification were performed on the HXB2 construct as a positive control. MW, molecular weight markers; nt, nucleotides. (B) RNA of H9 cell lysates from mock-infected cells or cells expressing the wild type or vif mutant were subjected to RNase protection with a probe to the HIV-1 genome. (C) Western blot analysis of cell lysates was performed with antiserum against Vif. (D) Amino acid sequence alignment of HIV-1 Vif and Xlrbpa. Residues in boldface display the highly conserved Vif sequence among lentiviruses. Shaded residues display sequence identity between HIV-1 Vif and Xlrbpa.