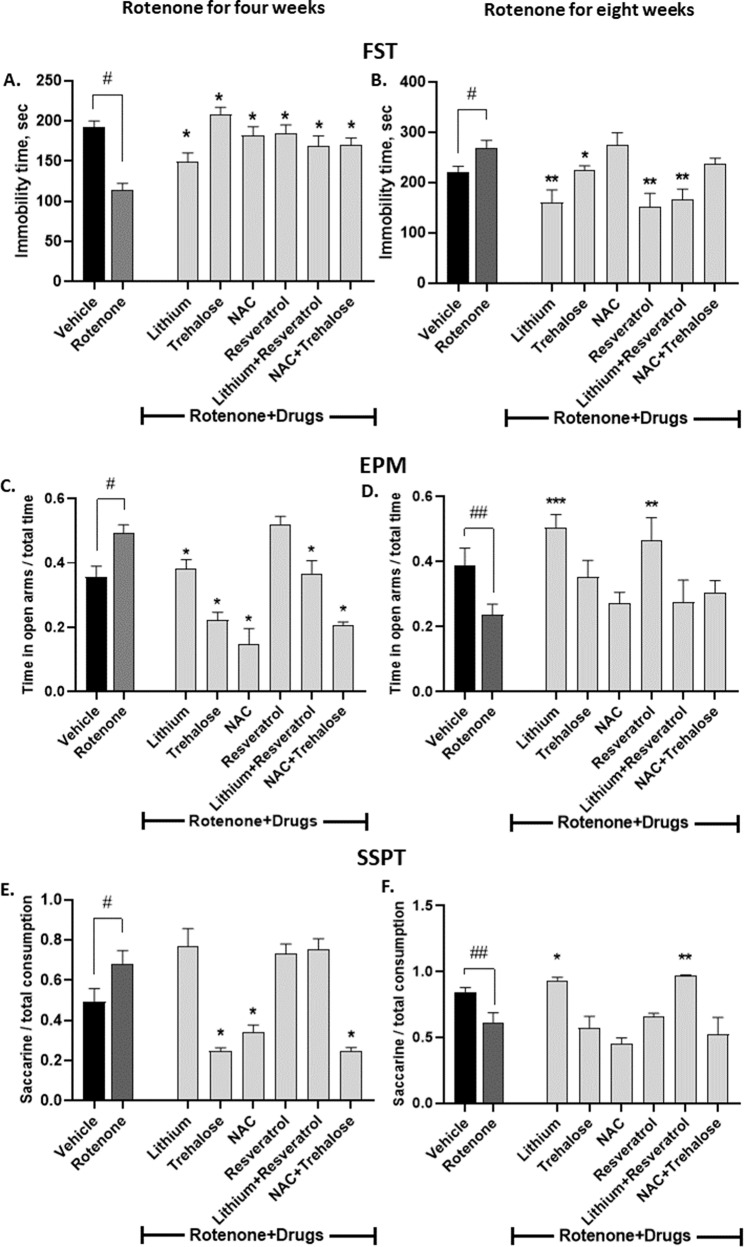
Fig. 1. Some of the drugs and some of their combinations administered during the last week/two weeks of rotenone treatment for four (A, C, E) or eight (B, D, F) weeks attenuated rotenone’s effect in the FST, EPM and SSPT.
Results represent means ± SEM of at least 7 mice/group. Our previous results [6] that four and eight weeks of rotenone treatment decreases and increases, respectively, the immobility time of the mice in the FST (A, B), and increases and decreases, respectively, the time spent in the open arms of the EPM (C, D), increases and decreases, respectively, the preference of the mice for sweet solution (E, F), and that lithium treatment attenuates rotenone’s effects in the FST and the EPM (A–D) were replicated. Two-ways ANOVA with rotenone (with/without) and drugs (with/without) as main factors: FST - A. rotenone effect, F(6,209) = 7.274, p < 0.0001; rotenoneXdrugs interaction, F(6,09) = 7.966, p < 0.0001. B Rotenone effect, F(6,111) = 13.21, p < 0.0001; rotenoneXdrugs interaction, F(6,111) = 2.557, p = 0.02. EPM. C Rotenone effect, F(6,166) = 27.13, p < 0.0001; rotenoneXdrugs interaction, F(6,166) = 6.234, p < 0.0001; drugs effect, F(1,166) = 8.449, p = 0.0042. D Rotenone effect, F(6,114) = 5.31, p = 0.0001; rotenoneXdrugs interaction, F(6,114) = 2.978, p < 0.01. SSPT. E Rotenone effect, F(6,81) = 16.53, p < 0.0001. F Rotenone effect, F(6,36) = 6.856, p < 0.0001; drugs effect, F(1,36) = 11.42, p = 0.0018. Asterisks and symbols denote results of Fisher’s LSD post-hoc test: #p < 0.05 and ##p < 0.001 - vs. vehicle; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.001, and ***p < 0.0001 – vs. rotenone.