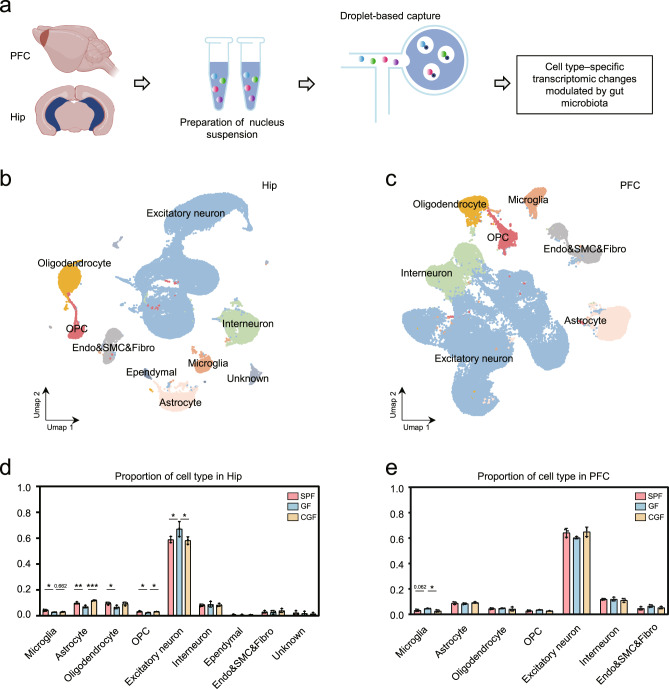
Fig. 1. Gut microbiota absence changed microglial proportion in the Hip and PFC.
a Schematic graph shows the workflow of acquiring hippocampus (Hip) and prefrontal lobe cortex (PFC) samples, nuclei isolation and droplet-based capture (10X Genomics) to produce cell type–specific transcriptomic signatures. b, c UMAP graph-based clustering and visualization of all captured nuclei for the Hip (b) and PFC (c). CNS resident cell types included excitatory neuron, interneuron, microglia, astrocyte, oligodendrocyte, OPC, ependymal cell, endothelial cell, smooth muscular cell, and fibroblast (Endo&SMC&Fibro). d In the Hip, GF mice had significantly decreased microglial proportion than SPF mice, and microbial colonization failed to rescue this change. The downregulated hippocampal astrocyte and OPC proportion in GF group relative to the SPF group were reversed by microbial colonization in the CGF group (SPF, n = 3; GF, n = 3; CGF, n = 3; data are mean ± SEM; GF vs. SPF, microglia, *P = 0.013, Excitatory neuron, *P = 0.0444, astrocyte, **P = 0.005, oligodendrocyte, *P = 0.0394, OPC, *P = 0.015; GF vs. CGF, microglia, P = 0.662, astrocyte, ***P = 0.0003, Excitatory neuron, *P = 0.0342, OPC, *P = 0.034; P values are from ANOVA post hoc analysis-LSD test). e In the PFC, there was an increased trend of proportion of microglia in GF group relative to SPF groups, which could be reversed by microbial colonization (SPF, n = 3; GF, n = 3; CGF, n = 3; data are mean ± SEM; GF vs. CGF, microglia, *P = 0.021; P values are from ANOVA post hoc analysis-LSD test).