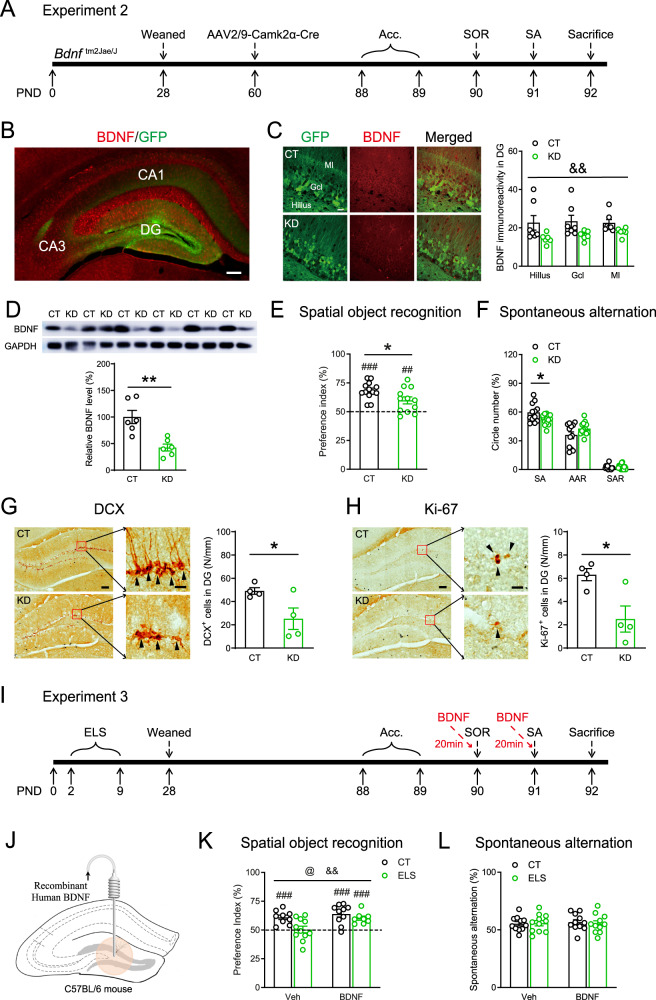
Fig. 2. BDNF in the DG mediated early-life stress-induced spatial memory impairment.
A The experimental timeline of the behavioral procedure and brain tissue acquisition after viral injection. B Region-specific expression of GFP in the DG is shown. Scale bar = 200 µm. C Representative images showing the expression of BDNF and GFP in the DG of CT and KD mice. Immunostaining analyses confirmed knockdown-induced reduction of BDNF expression in the DG. Scale bar = 20 µm. D Western blot analyses confirmed the knockdown-induced reduction of BDNF expression in the DG. E In the SOR test, although both CT and KD mice showed preference to the novel location, CT mice had higher preference index than KD mice. F KD mice had a lower spontaneous alternation ratio in the Y-maze test than control mice. BDNF knockdown decreased the number of DCX-positive (G) and Ki-67-positive (H) neurons in the DG (arrowheads). Scale bar = 100 µm or 20 µm. I The experimental timeline of the behavioral procedure and rhBDNF infusion after ELS exposure. J Schematic showing the DG local injection of rhBDNF in adult C57BL/6N mice. K In the SOR test, except that the ELS + Veh group failed to recognize the object placed in novel location, the other three groups performed well. L ELS or rhBDNF did not affect the spontaneous alternation ratio in the Y-maze test. AAR alternate arm return, Acc. acclimation, BDNF brain-derived neurotrophic factor, CT control, DCX doublecortin, DG dentate gyrus, ELS early-life stress, gcl granule cell layer, ml molecular layer, KD knockdown, OF open field, PND postnatal day, SA spontaneous alternation, SAR same arm return, SOR spatial object recognition, Veh vehicle. *p < 0.05, unpaired t test; ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001, one-sample t test; &&p < 0.01, the main effect of virus.