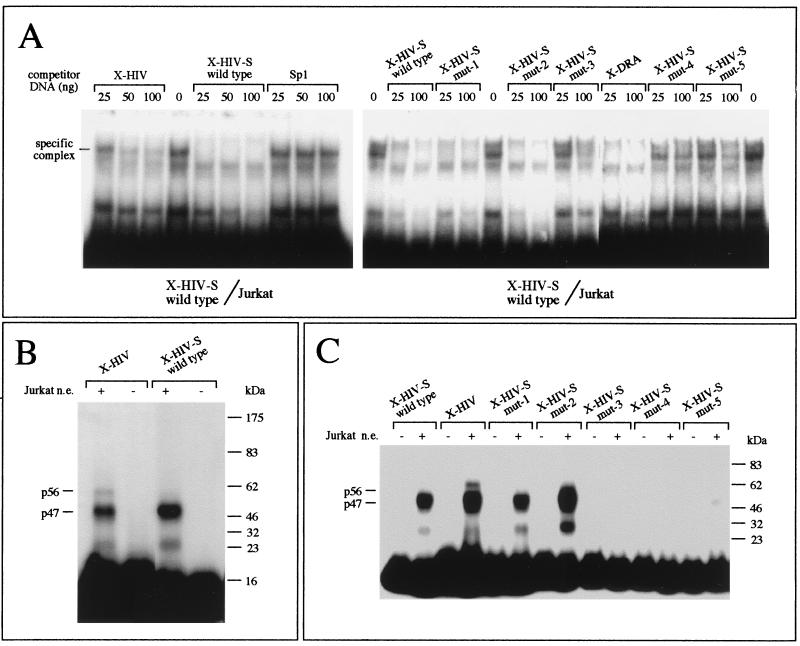
FIG. 7.
(A) Competitive band shift assay. The binding of nuclear proteins from Jurkat cells to short double-stranded oligonucleotides carrying the XMAS motif (without flanking regions [X-HIV-S wild type]) was inhibited by addition of a molar excess of unlabeled X-HIV, X-HIV-S wild type, or HIV-1 Sp1-binding site-containing (Sp1) double-stranded oligonucleotide (left panel); in the right panel, the binding was inhibited by addition of a molar excess of unlabeled X-HIV-S wild type or mutants (X-HIV-S mut-1 to mut-5) carrying dinucleotide substitution involving the HIV-1 XMAS motif. (B) The sizes of the DNA-binding proteins contacting the X-HIV or the X-HIV-S wild type double-stranded oligonucleotide were compared by a UV cross-linking assay. The radiolabeled probes were incubated in the presence (+) or in the absence (−) of crude nuclear extracts (n.e.) from Jurkat cells. After the binding reaction, the assembled protein-DNA complexes were cross-linked by UV light exposure. The migration of the protein size markers is shown on the right side of the autoradiograph. The sizes of the protein-DNA complexes detected are reported on the left side of the autoradiograph. (C) The sizes of the DNA-binding proteins contacting the X-HIV-S wild type or mutant double-stranded oligonucleotides were compared by a UV cross-linking assay, as described above.