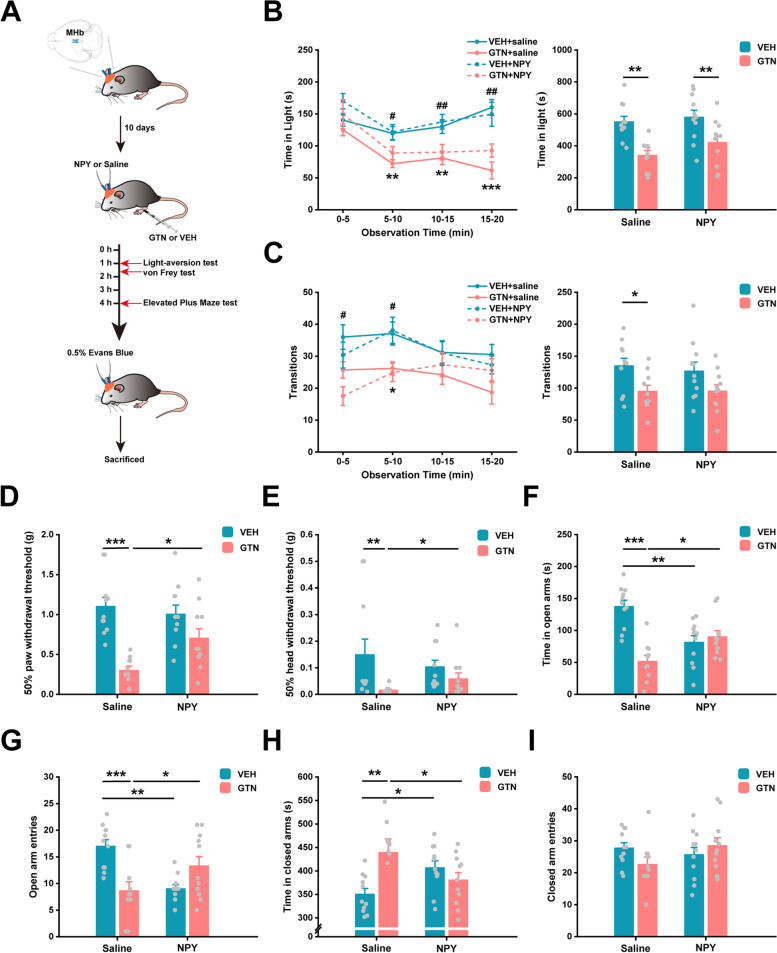
Fig. 5.
Microinjection of NPY into the MHb alleviates GTN-induced allodynia and anxiety-like behaviors. A Plan of the experimental procedure: MHb microinjections were performed immediately before VEH or GTN injection. B and C Effects of NPY or saline on time spent in light (B) and the number of transitions between zones (C) expressed as the average for each group per 5-min interval (left panel) and during a total of 20 min (right panel) in a light-aversive test at 1 h after VEH or GTN injection. D and E Effects of NPY or saline on the left hind paw (D) and head withdrawal thresholds (E) during the von Frey test at 1.5 h after VEH or GTN injection. F-I Effects of NPY or saline on time spent in the open arms (F), the number of open arm entries (G), time spent in the closed arms (H), and the number of closed arm entries (I) during the EPM test at 4 h after VEH or GTN injection. VEH + saline, n = 11 mice; GTN + saline, n = 10 mice; VEH + NPY, n = 11 mice; GTN + NPY, n = 11 mice. Significance was assessed by two-way repeated-measures ANOVA with post hoc comparison between groups (B and C left panel; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 VEH + saline versus GTN + saline; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 VEH + NPY versus GTN + NPY) or by two-way ANOVA with post hoc comparison between groups (B and C right panel, D, F-I; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001) or by Kruskal–Wallis H test with Mann–Whitney U post hoc comparison between groups (E; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01). All data are presented as the mean ± S.E.M