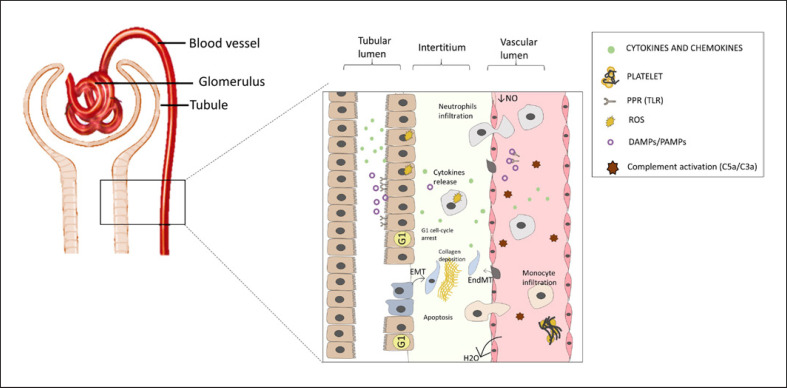
Fig. 1.
Pathophysiology of SI-AKI. SI-AKI is recognized by a complex mechanism characterized by the interplay between resident renal cells and immune system. Hyperinflammation is a physiological stimulus triggered by sepsis injury and is characterized by a humoral and a cellular mediator which exacerbate the renal injury. Hyperinflammation leads to neutrophil and macrophage/lymphocyte infiltration followed by organ failure. PAMPs/DAMPs interaction with tubular injured cells via PRRs enhances the inflammatory damage by stimulating the production of cytokines and adhesion molecules. On the other hand, DAMP/PAMP interaction with proximal TECs results in ROS production, apoptosis, and cell cycle arrest.