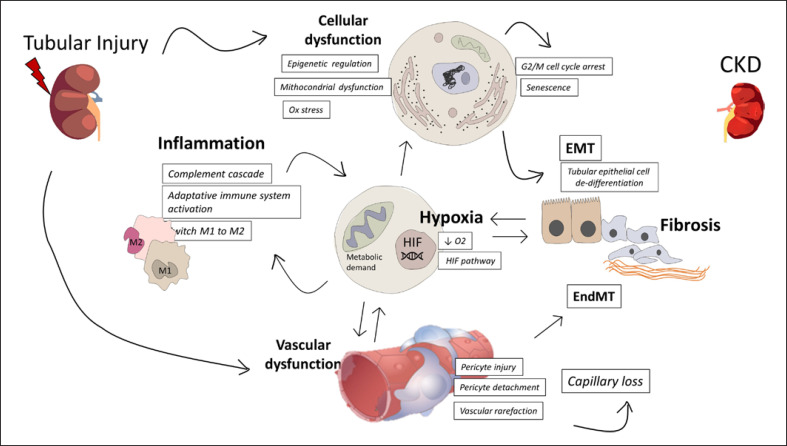
Fig. 2.
Pathophysiological mechanism involved in the AKI-to-CKD transition. Several mechanisms contribute to maladaptive repair to AKI leading to CKD progression. Main mechanism includes inflammation, hypoxia, vascular rarefaction, and cellular dysfunction which ultimately lead to kidney fibrosis. HIF, hypoxia-inducible factor; EMT, epithelial/mesenchymal transition; EndMT, endothelial/mesenchymal transition.