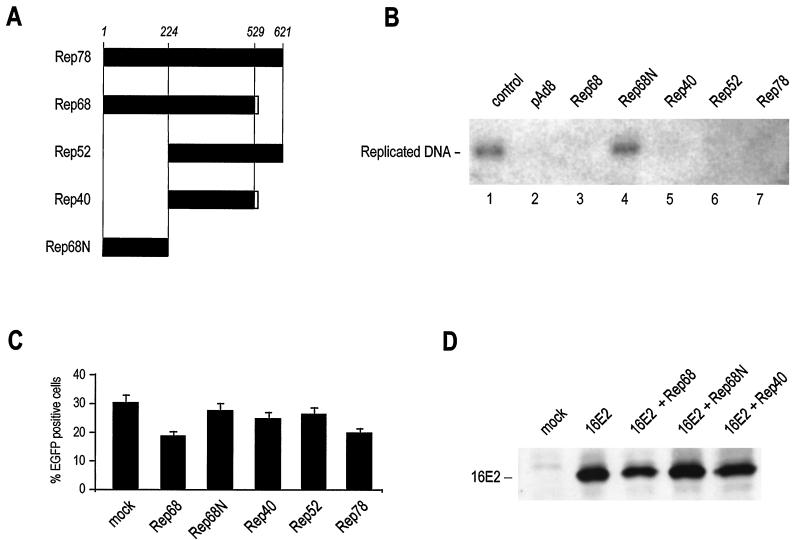
FIG. 1.
Rep proteins inhibit HPV16 replication. (A) Schematic representation of Rep proteins from AAV2. AAV2 has four overlapping Rep proteins: the two major products Rep78 and Rep68 and the two minor variants Rep52 and Rep40, which represent the C-terminal portions of Rep78 and Rep68, respectively. In this work, the N terminus of Rep78 or Rep68 (amino acids 1 to 224) was also expressed independently and termed Rep68N. All constructs were either used as GST fusion proteins in the in vitro binding studies or transiently expressed from a CMV promoter in cells. (B) Rep proteins inhibit HPV16 replication. 293 cells were transfected with an HPV16 ori-containing plasmid together with 16E1, 16E2, and the indicated Rep variants. Low-molecular-weight DNA was digested with DpnI, and replicated DNA was detected by Southern blot hybridization. (C) Short-term Rep expression does not induce nonspecific cellular toxicity. To verify that the observed inhibition of HPV16 replication by the Rep forms shown in panel B was not related to nonspecific cytotoxic effects, the indicated Rep plasmids were transfected with 1 μg of plasmid pEGFP-N1, expressing EGFP under the control of the CMV promoter. The number of fluorescent cells was measured after 48 h. Experiments were performed in triplicate; the mean and standard deviation values are shown for each point. (D) Changes in 16E2 expression do not account for Rep-induced inhibition of HPV16 replication. Western blotting experiments with anti-16E2 antibodies were performed 48 h after transfection of the indicated Rep forms.