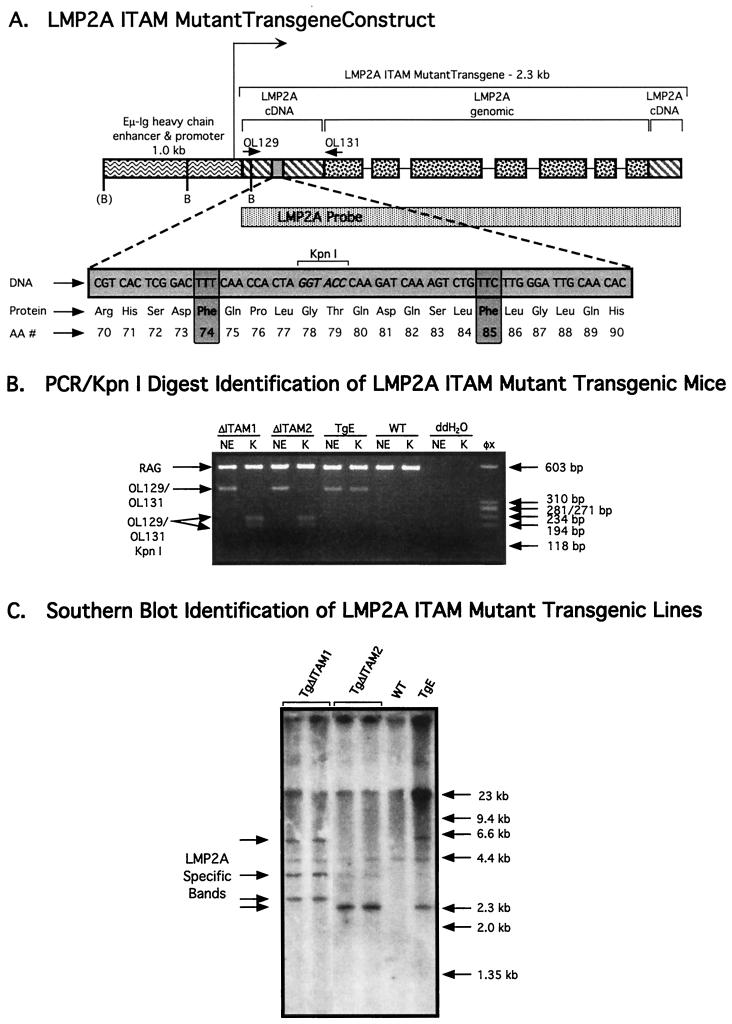
FIG. 1.
Generation of LMP2A ITAM mutant transgenic mice. (A) LMP2A ITAM mutant transgene construct. The Eμ heavy-chain enhancer/promoter (wavy lines) was fused to the LMP2A ITAM mutant transgene containing both LMP2A cDNA sequences (striped lines) and EBV genomic sequences (stippled). The DNA, protein, and amino acid number (AA #) for the altered ITAM sequences are shown in the shaded inset at the bottom. A silent point mutation creates a KpnI site in the LMP2A ITAM mutant transgene, which aids in distinguishing ITAM mutant mice from LMP2A transgenic mice by PCR using OL129 and OL131 (upper inset) followed by KpnI digestion. The LMP2A cDNA probe shown spans sequences throughout the LMP2A transgene. BamHI (B) sites are indicated. The BamHI site in parentheses may be lost upon integration. (B) PCR/KpnI digest identification of LMP2A ITAM mutant transgenic mice. Tail genomic DNA sequences from LMP2A ITAM mutant, nonmutated LMP2A, and WT littermate control animals were amplified using OL129-OL131 and RAG positive control primers, followed by digestion with KpnI (K) or no enzyme (NE). Identities of the amplified products and their subsequent digested fragments are shown to the left. φX DNA digested with HaeIII was used as a size standard (right-most lane). (C) Southern hybridization analysis of LMP2A ITAM mutant lines. Tail DNAs from TgΔITAM1, TgΔITAM2, TgE, and WT animals were digested with BamHI, run on an 0.8% agarose gel, and probed for LMP2A sequences by Southern hybridization. Size standards are indicated at the right.