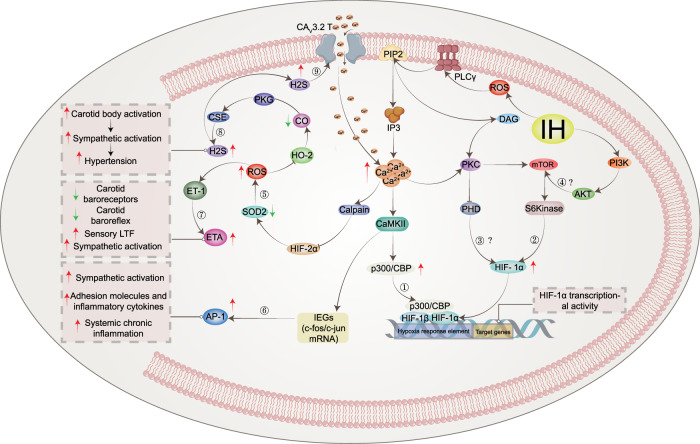
Fig. 3.
Activation of IH-associated signaling pathways. IH causes an increase in intracellular ROS, which can activate PLC-γ to produce IP3 and DAG. These two messengers are involved in intracellular signal transduction pathways and induce HIF-1α protein expression and transcriptional activity, respectively. Pathway ① indicates that IH-induced transactivation of HIF-1α requires ROS-mediated phosphorylation of the CaMKII-dependent coactivator p300. Pathway ② indicates that hypoxia-induced HIF-1α protein expression is caused by increased synthesis of mTOR, which is dependent on the ROS/Ca2+ signaling pathway. However, the mechanism by which PKC inhibits the reduction in PHD and the mechanism of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway needs to be further confirmed (③④). Pathway ⑤ indicates that calcium-activated calpain promoted the degradation of HIF-2α protein in arterial corpuscles, resulting in a decrease in SOD2 and impaired antioxidant capacity of cells. Pathway ⑥ indicates that CaMKII can activate IEG genes, increase the transcription of c-fox mRNA or c-jun mRNA and increase the expression of AP-1, which is related to the activation of the sympathetic system and systemic inflammation. Pathway ⑦ indicates that increased ROS could stimulate the increased expression of ET and ETA and induce LTF in the carotid body. Pathway ⑧ indicates that IH causes ROS-dependent inhibition of CO production by HO-2, resulting in a decrease in PKG activity and an increase in H2S produced by CSE, which triggers a chemosensory reflex of the carotid body, leading to sympathetic excitation and hypertension. In addition, elevated H2S could activate the CAV3.2 T calcium channel on the cell membrane, causing Ca2+ influx and further aggravating the damage caused by IH (⑨). IH intermittent hypoxia, PLC-γ phospholipase C γ, PIP2 phosphatidylinositol (4,5) bisphosphate, IP3 inositol-3-phosphate, CaMKII calmodulin-dependent kinase II, IEGs immediate early genes, AP-1 activator protein-1, SOD2 superoxide dismutase 2, ET-1 endothelin 1, ETA endothelin receptor, HO-2 heme oxygenase-2, CO carbon monoxide, PKG: protein kinase G, CSE cystathionine γ-lyase, H2S hydrogen sulfide, LTF long-term facilitation