Figure 2.
Impact of miR-132 depletion in the hippocampus
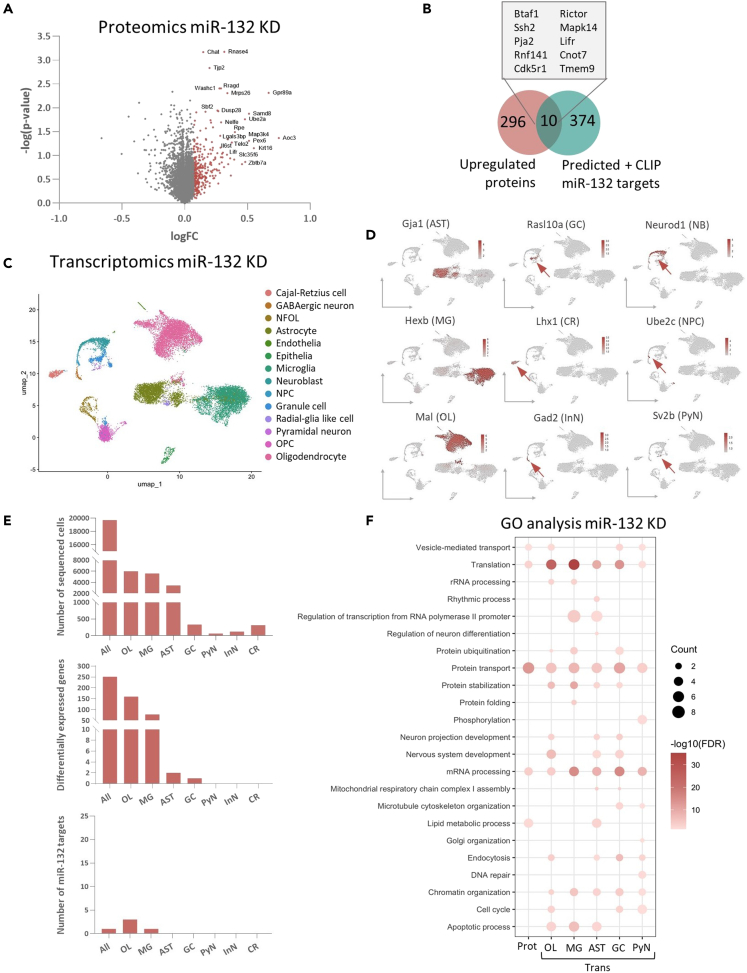
(A) Differentially expressed proteins upon miR-132 KD presented in a volcano plot. The top 5% of proteins anticorrelated to miR-132 are indicated in red.
(B) Identification of putative miR-132 targets from intersection with 5% most upregulated proteins and the list of identified predicted miR-132 targets.
(C) UMAP visualization of 19,705 isolated mouse hippocampal miR-132 KD and corresponding control single-cell transcriptomes. Cells are colored by identified cell type. NFOL, newly formed oligodendrocyte; NPC, neuronal precursor cell; OPC, oligodendrocyte precursor cell.
(D) UMAP plots colored by the normalized expression level of cell type-specific marker genes used for cluster annotation. Arrows indicate the cell cluster of interest.
(E) Number of cells, number of significant DEGs (Wilcoxon rank-sum test using Bonferroni for p value correction, adjusted p value <0.05 considered significant), or amount of putative miR-132 targets identified by intersection with predicted miR-132 targets, as included in the scRNAseq analysis. Counts correspond to all cells pseudo-bulked together (All) or to each cell type.
(F) GO biological processes significantly enriched in differentially expressed proteins (Prot) or genes (Trans) in distinct cell types. Count represents the % of included proteins/genes that are part of each process. Color represents significance, top 20 GO terms are displayed (Fisher’s Exact test, p values corrected with FDR, adjusted p value <0.05 considered significant). AST, astrocyte; GC, granule cell; NB, neuroblast; MG, microglia; CR, Cajal-Retzius neuron; NPC, neuronal precursor cell; OL, oligodendrocyte; InN, inhibitory/GABAergic neuron; PyN, hippocampal pyramidal neuron. See also Figures S1, S2, Tables S2, and S3.