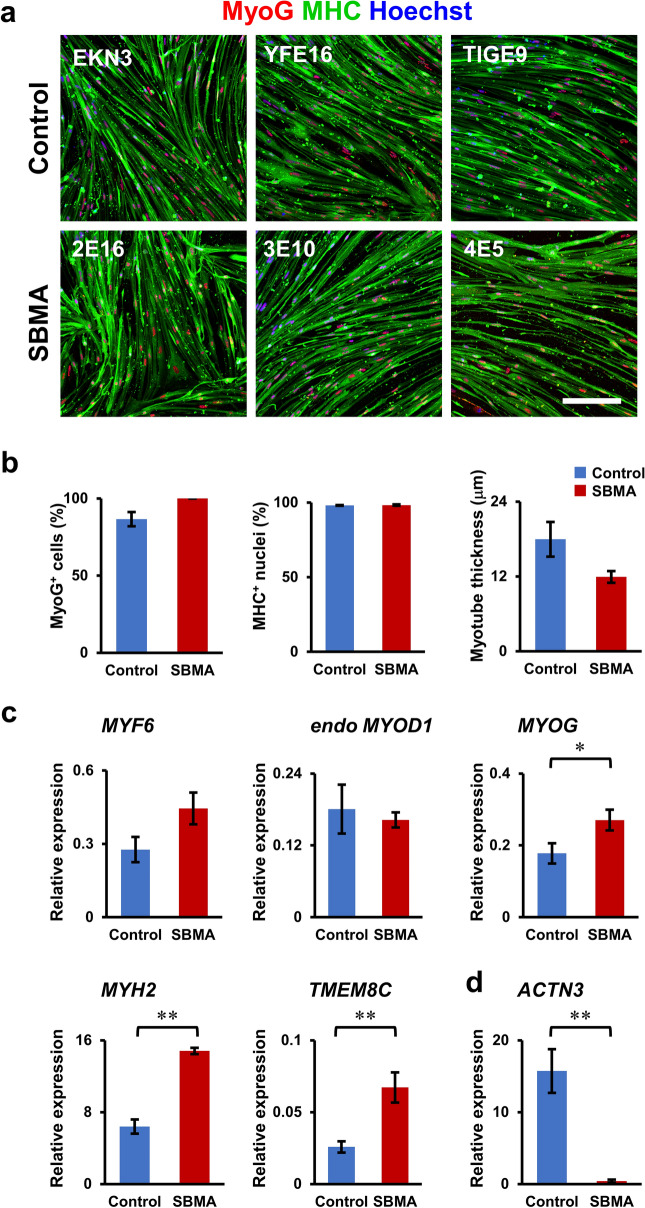
Figure 6.
SBMA disease-specific hiPSCs efficiently differentiated into mature skeletal muscle and exhibited reduced ACTN3 expression, consistent with the decrease in fast-twitch muscle in SBMA patients. (a) ICC analysis of MyoG (red) and MHC (green) in skeletal muscles derived from SBMA disease-specific hiPSCs and control hiPSCs. SBMA disease-specific hiPSCs could differentiate into mature skeletal muscles as efficiently as control hiPSCs. Scale bar, 200 μm. (b) Quantitative analysis of the parameters of skeletal muscle differentiation (MyoG+ cells and MHC+ nuclei) and maturation (thickness of myotubes). The data are presented as the mean ± SEM, n = 3. (c,d) Quantitative RT‒PCR analysis of SBMA and control hiPSC-derived skeletal muscles for MYF6, endo-MYOD1, MYOG, MYH2, and TMEM8C. (c) and ACTN3 (d) expressed in fast-twitch muscles. The data are presented as the mean ± SEM, n = 9 (n = 3 each from 3 patients and 3 controls). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.