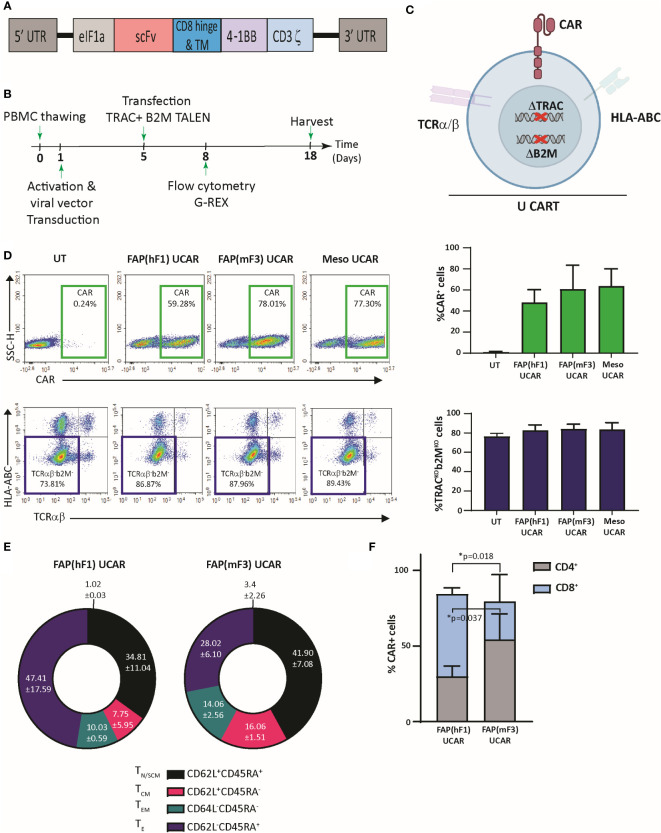
Figure 1.
TALEN-mediated multiplex editing generates universal immune evasive CAR T-cells against solid tumor targets. (A) Lentiviral CAR construct for T cell transduction comprised of the anti-tumor targeting single-chain variable fragment (scFv), human CD8α hinge and transmembrane domain, a human 4-1BB costimulatory domain, and a human CD3ζ activation domain. (B) Experimental strategy for TALEN-mediated gene editing, lentiviral transduction, expansion, and analysis of engineered human universal CAR T-cells. (C) Pictorial representation of immune evasive, universal CAR T-cells engineered with lentiviral CAR expression and TALEN-mediated multiplex editing of TRAC and B2M gene loci, resulting in downregulation of surface TCRα/β and HLA-ABC. (D) Top panel, flow-cytometry plots showing frequency of CAR expression among viable engineered T cells (left), and associated quantitation (right). Bars show the means ± SD, n=3. Bottom panel, flow-cytometry plots showing frequency of TCRα/β (-)/HLA-ABC (-) viable engineered T cells (left) and associated quantitation (right). Bars show means ± SD, n=3. (E) Frequency of FAP UCAR T-cell subpopulations displaying CD62L+CD45RA+ (TN naive-like/TSCM memory stem cell), CD62L+CD45RA− (TCM central memory), CD62L-CD45RA− (TEM effector memory) and CD62L-CD45RA+ (TE terminal effector) labeling at end of engineered T cell expansion (n=2). (F) Frequency of FAP UCAR T-cell CD4+ and CD8+ subpopulations (n=3). Bars show the means ± SEM; P-values determined by Student t test (two-tailed, unpaired). *P < 0.05.