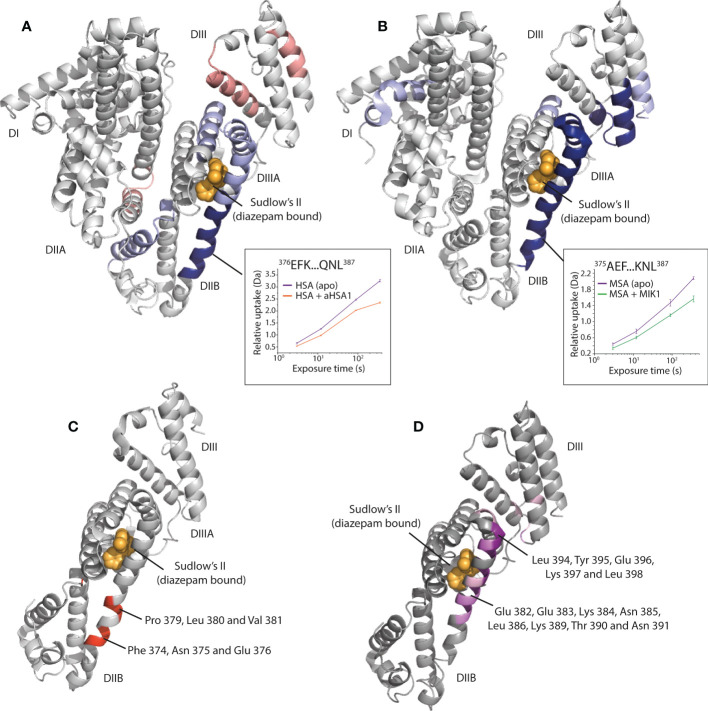
Figure 4.
Epitope mapping of the aHSA and aMSA binding sites on serum albumin. (A) shows HDX data for aHSA coloured onto a human serum albumin crystal structure (PDB: 1AO6) (20). Sudlow’s site II with diazepam bound (PDB: 2BXF) (21) is shown for reference, diazepam was not used in the experiments and is shown to illustrate the position of Sudlow’s II. Areas of solvent protection and deprotection are coloured blue or red, respectively, by relative intensity. A clear area of protection suggests the epitope is present within the DIIB domain, adjacent to Sudlow’s II. (B) shows HDX data for aMSA coloured onto an AlphaFold (22) model of MSA, where a clear area of protection is again visible on the DIIB domain. (C, D) show the position of scanning alanine mutations on the DII/DIII domains of HSA and MSA, respectively. Mutations which attenuated binding of the FabT knob domain fusion proteins are in shown in red on HSA for FabT-aHSA and in purple on MSA for FabT-aMSA. These areas are contained within the areas of solvent protection as predicted by HDX.