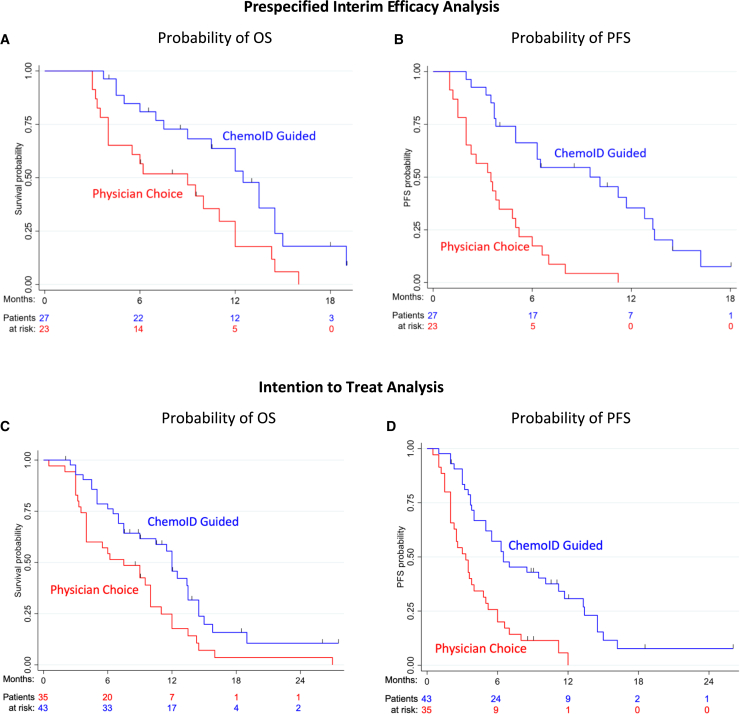
Figure 3.
OS and PFS are significantly improved by ChemoID-guided therapy
(A) Prespecified interim efficacy analysis of OS. The number of events; median OS; OS rates at 0, 6, 12, and 18 months; and the Kaplan-Meier curve for OS in all patients treated with ChemoID-guided (blue) vs. physician-choice (red) therapies. Symbols, censored observations.
(B) Prespecified interim efficacy analysis of PFS. The number of events; median PFS; PFS rates at 0, 6, 12, and 18 months; and the Kaplan-Meier curve for PFS per investigator assessment in patients treated with ChemoID-guided (blue) vs. physician-choice (red) therapies. Symbols indicate censored observations.
(C) Intention-to-treat analysis of OS. The number of events; median OS; OS rates at 0, 6, 12, and 18 months; and the Kaplan-Meier curve for OS in all patients treated with ChemoID-guided (blue) vs. physician-choice (red) therapies. Symbols, censored observations.
(D) Intention-to-treat Analysis of PFS. The number of events; median PFS; PFS rates at 0, 6, 12, and 18 months; and the Kaplan-Meier curve for PFS per investigator assessment in patients treated with ChemoID-guided (blue) vs. physician-choice (red) therapies. Symbols indicate censored observations. A Cox proportional hazards model estimated hazard ratios (HRs) and CIs.