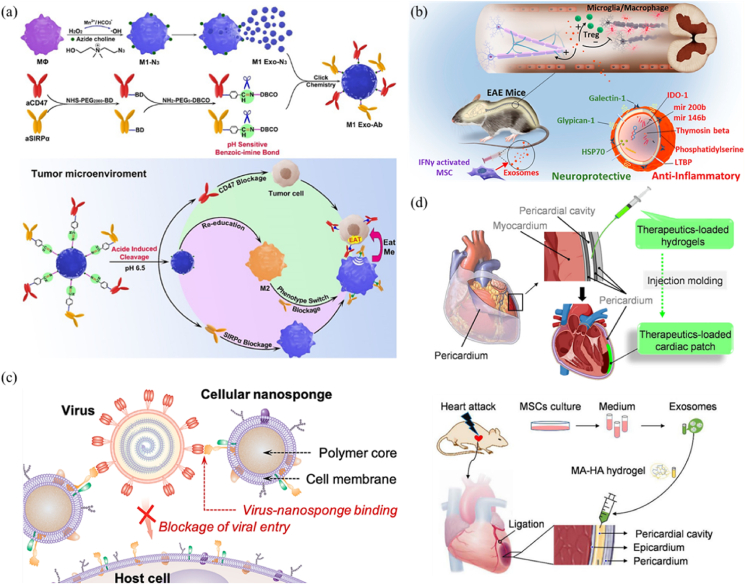
Figure 7.
Cellular nanovesicle-based immunomodulatory therapy for treating various disease, including cancer, autoimmune diseases, infectious diseases, and injury and trauma diseases. (a) Schematic illustration of M1-EVs engineered with CD47 and SIRPα antibodies for cancer immunotherapy. Reproduced with permission from Ref. 409. Copyright © 2020, Wiley. (b) Schematic illustration of the immunomodulatory effect of MSC-EVs on the proliferation of Tregs for treating multiple sclerosis. Reproduced with permission from Ref. 454. Copyright © 2019, American Chemical Society. (c) Schematic illustration of EVs expressing ACE2 and CD147 as nano-decoys to prevent SARS-CoV-2 from entering into host cells. Reproduced with permission from Ref. 472. Copyright © 2020, American Chemical Society. (d) Schematic illustration of MSC-EVs encapsulated into hydrogels and injected into the cardiac tissue for prolonged retention to treat heart attack. Reproduced with permission from Ref. 332. Copyright © 2021, Springer Nature.