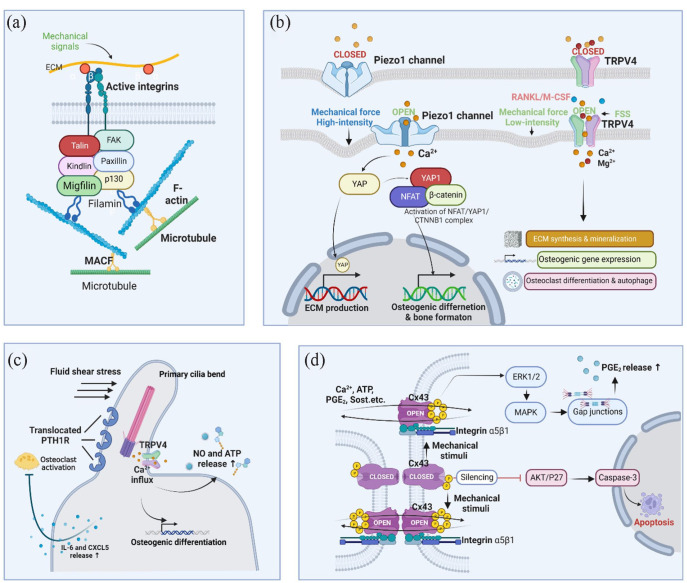
Figure 3.
Mechanosensitive structures. (a) Focal adhesions. Focal adhesions connect ECM mechanical signals to the cytoskeleton, affecting cytoskeleton arrangement and crosslinking; (b) Piezo1 and TRPV4. Activation of ion channels by mechanical stimuli elicits specific ion flow, especially calcium influx, to modulate downstream signaling pathways and cell differentiation; (c) Primary cilium. When primary cilia bend under FSS, TRPV4 ion channels open, allowing Ca2+ influx and MSCs osteogenic differentiation. PTH1R translocation on primary cilia prevents osteoclast activation by releasing IL-6 and CXCL5; (d) Cx43. When osteocytes experience mechanical stimulation, the Cx43 protein is phosphorylated, and the connexon is opened, allowing the exchange of several effectors, such as calcium, ATP, PGE2, and Sost, between connecting cells through gap junctions. Osteocytes with Cx43-silencing undergo apoptosis via AKT/P27/Caspase-3 pathway. The graph was created with BioRender.com.