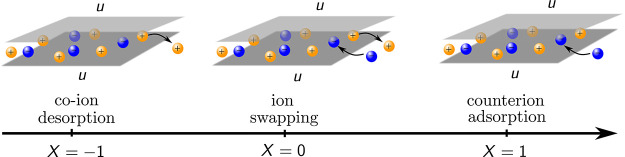
Figure 1.
Three basic mechanisms of nanopore charging. Schematics of co-ion desorption (X = −1), co-ions swapping for counterions (X = 0), and counterion adsorption (X = 1). u is the potential difference applied to the nanopore with respect to bulk electrolyte (not shown). The differential charging parameter X(u) is defined by eqs 7. A charging mechanism can be a combination of swapping and either adsorption (X > 0) or desorption (X < 0). Note that X can be smaller than −1 (larger than +1), in which case co-ion desorption (counterion adsorption) is accompanied by the desorption of counterions (adsorption of co-ions).