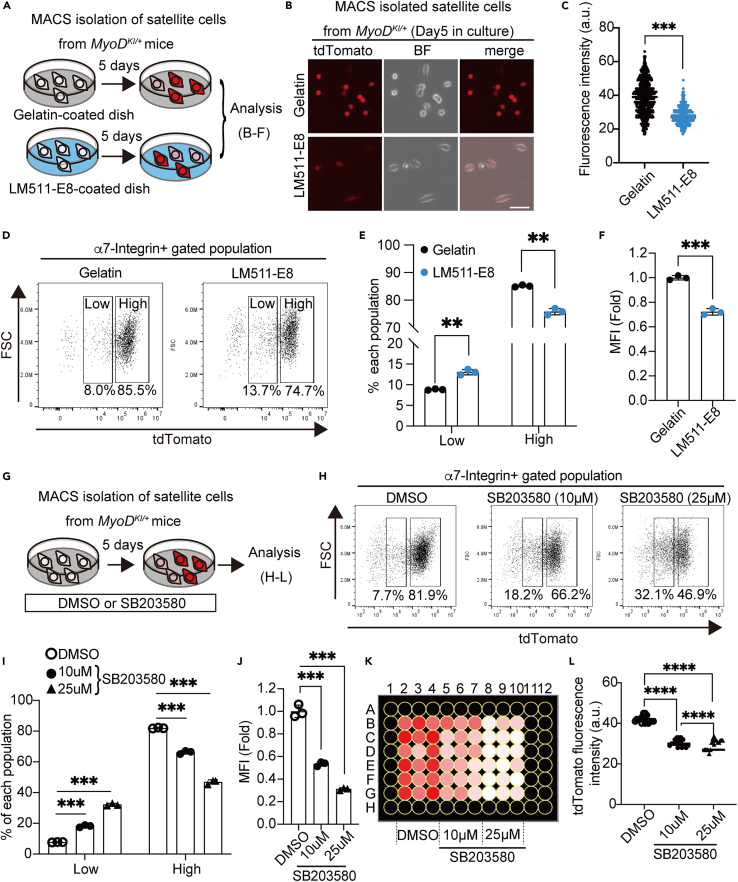
Figure 7.
MyoDKI/+ mice are useful for drug screening to manipulate MuSCs in vitro
(A) Schematic diagram of culture of MuSCs from MyoDKI/+ mice in gelatin- and LM-511-E8-coated dishes.
(B) Representative fluorescence images of MuSCs isolated from MyoDKI/+ mice and cultured for 5 days in either gelatin- or LM511-E8-coated dishes. Scale bar: 50 μm.
(C) Quantification of MyoD-tdTomato fluorescence intensity in MuSCs in (B) (Gelatin, n = 717; LM511-E8, n = 446).
(D) Representative flow cytometry plot of cultured MuSCs isolated from MyoDKI/+ mice in either gelatin- or LM511-E8-coated dishes.
(E and F) Quantification of MyoD-tdTomatoLow and MyoD-tdTomatohigh fractions (E) and MFI (F) in (D). The gate is defined based on the WT-derived MuSCs analysis. (n = 3 mice per group).
(G) Schematic diagram of culture of MuSCs from MyoDKI/+ mice in the presence of DMSO or SB203580.
(H) Representative flow cytometry plot of MuSCs isolated from MyoDKI/+ mice and cultured for 5 days with 10, 25 μM of SB203580, or DMSO control.
(I–K) Quantification of MyoD-tdTomatoLow and MyoD-tdTomatohigh fractions (I) and MFI (J) in H (n = 3 mice per group). (K) MuSCs from MyoDKI/+ mice are cultured in a 96-well-plate for 5 days with 10, 25 μM of SB203580, or DMSO control. MyoD-tdTomato fluorescence intensity is visualized as heatmap.
(L) MyoD-tdTomato fluorescence intensity of each well in K is quantified. All data are represented as the mean ± s.e.m. ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001.