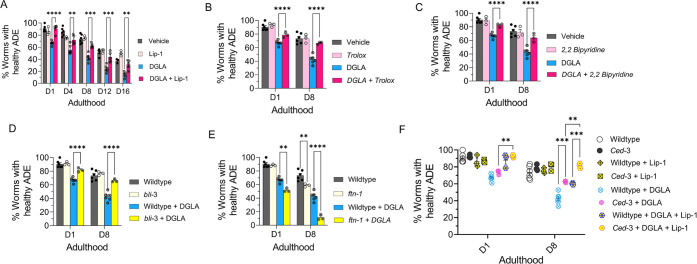
Figure 2.
DGLA induces neurodegeneration in dopaminergic neurons via ferroptosis. (A) Percentage (%) of worms with healthy ADE neurons of worms exposed to 100 μM DGLA ± 250 μM liproxstatin-1. (B) Percentage (%) of worms with healthy ADE neurons in wild-type C. elegans treated with 100 μM DGLA ± 500 μM Trolox (vitamin E). (C) Percentage (%) of worms with healthy ADE neurons for Pdat-1::gfp worms treated with 100 μM DGLA ± 100 μM 2,2′-bipyridine. (D) Percentage (%) of worms with healthy ADE neurons in Pdat-1::gfp and Pdat-1::gfp;bli-3 worms treated with 100 μM DGLA. (E) Percentage (%) of worms with healthy ADE neurons for Pdat-1::gfp and Pdat-1::gfp;ftn-1 worms treated with 100 μM DGLA. (F) Percentage (%) of worms with healthy ADE neurons with Pdat-1::gfp and Pdat-1::gfp;ced-3 worms treated with 100 μM DGLA ± 250 μM liproxstatin-1. All supplementations were done at the L4 stage. Two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), Tukey’s multiple comparison test. *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001, ****P < 0.0001; NS, not significant. DGLA, Dihomo-γ-linolenic acid; LA, linoleic acid; EPA, eicosapentaenoic acid; Lip-1, liproxstatin-1.