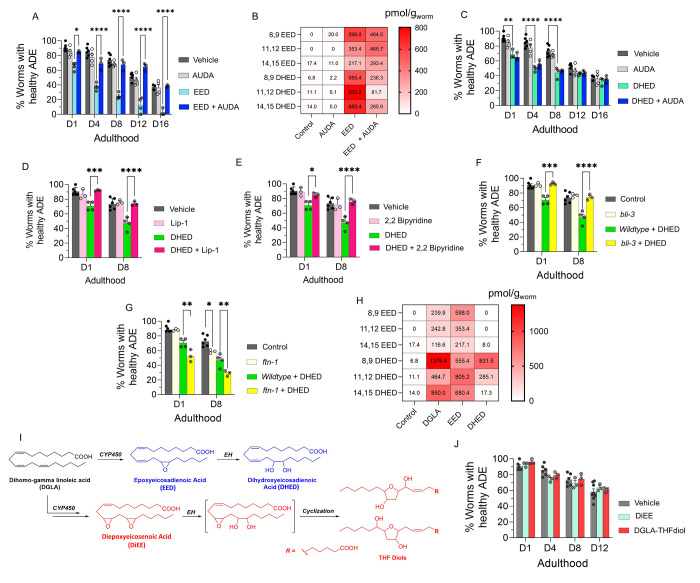
Figure 4.
DHED, dihydroxy fatty acid downstream of DGLA/EED, is key candidates for neurodegeneration induced by DGLA in dopaminergic neurons. (A) Percentage (%) of worms with healthy ADE neurons in Pdat-1::gfp worms treated with 100 μM EED ± 100 μM AUDA. (B) Oxylipin profile representing pmol/g of EED and DHED regioisomers in worms treated with 100 μM EED ± 100 μM AUDA compared to control. (C) Percentage (%) of worms with healthy ADE neurons for Pdat-1::gfp treated with 100 μM DHED ± 100 μM AUDA. (D) Percentage (%) of worms with healthy ADE neurons of worms exposed to 100 μM DHED ± 250 μM liproxstatin-1. (E) Percentage (%) of worms with healthy ADE neurons for Pdat-1::gfp worms treated with 100 μM DHED ± 100 μM 2,2′-bipyridine. (F) Percentage (%) of worms with healthy ADE neurons for Pdat-1::gfp and Pdat-1::gfp;ftn-1 worms treated with 100 μM DHED. (G) Percentage (%) of worms with healthy ADE neurons in Pdat-1::gfp and Pdat-1::gfp;bli-3 worms treated with 100 μM DHED. (H) Oxylipin profile representing the pmol/g of EED and DHED regioisomers in worms treated with 100 μM DGLA, EED, and DHED compared to control. (I) Two possible metabolisms of DGLA through the CYP/EH pathways; the alternative metabolism is that CYP can do two consecutive oxidations (or under oxidative stress) to yield diepoxies EED, after which EH will open one epoxide which under physiological conditions can cyclize to THF diols. (J) Percentage (%) of worms with healthy ADE neurons for Pdat-1::gfp treated with 100 μM DiEE and 100 μM DGLA-THF diol. All supplementations were done at the L4 stage. Two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), Tukey’s multiple comparison test. *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001, ****P < 0.0001; without *, not significant. DGLA, Dihomo-γ-linolenic acid; EED, epoxyeicosadienoic acid; DHED, dihydroxyeicosadienoic acid; CYP, cytochrome P450; EH, epoxide hydrolase; AUDA, 12-(1-adamantane-1-yl-ureido-) dodecanoic acid; DiEE, diepoxyeicosadienoic acid.