FIGURE 1.
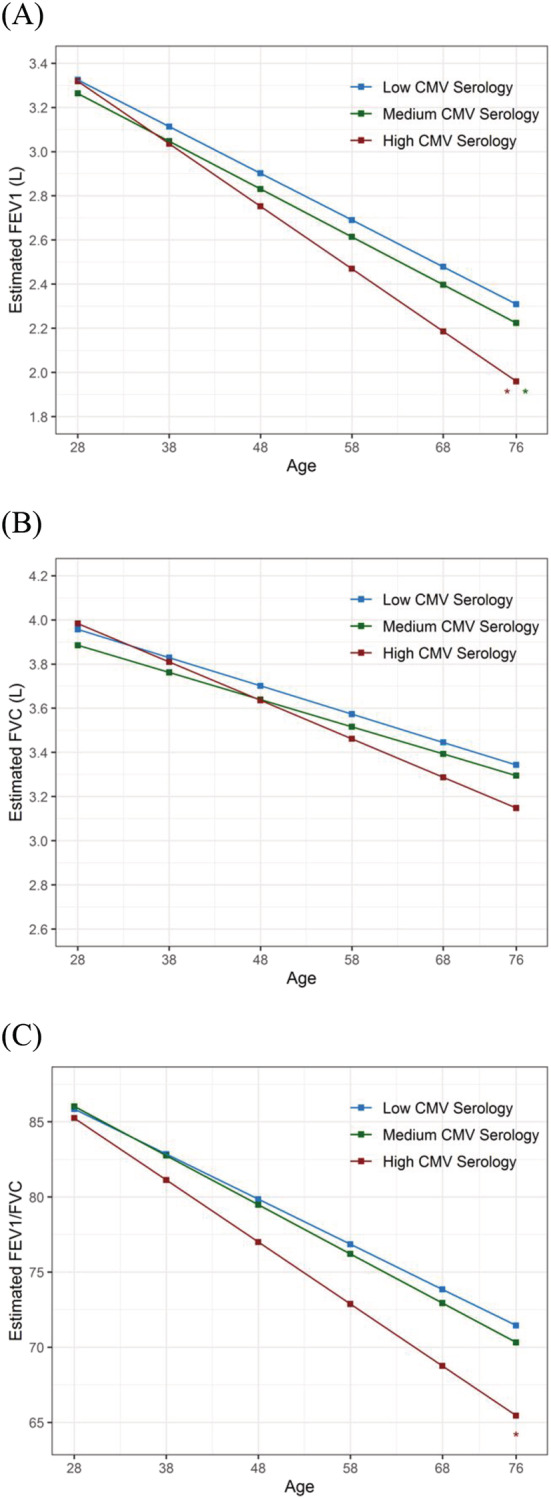
Levels and decline of (A) FEV1, (B) FVC, and (C) FEV1/FVC ratio in adult life in TESAOD participants across tertiles of CMV serology at baseline. ** FEV1 decline significantly steeper for the high CMV serology group than for the low and medium CMV serology groups. * FEV1/FVC decline significantly steeper for the high CMV serology group than for the low CMV serology group. Data are estimated from fully adjusted random coefficients models including 403 participants with multiple lung function tests for a total of 2908 observations. Models included interaction terms between CMV serology tertiles and age to test differences in decline and they were further adjusted for sex, height, body mass index categories at enrollment, level of education, smoking status, pack‐years, and serum CRP at enrollment. Lines represent predicted values for a 170‐cm tall female with geometric mean CRP levels of 1.35 mg/L at baseline and ≥12 years of education. CMV, cytomegalovirus; TESAOD, Tucson Epidemiological Study of Airway Obstructive Disease; FEV1, forced expiratory volume in 1 s; FVC, forced vital capacity.
