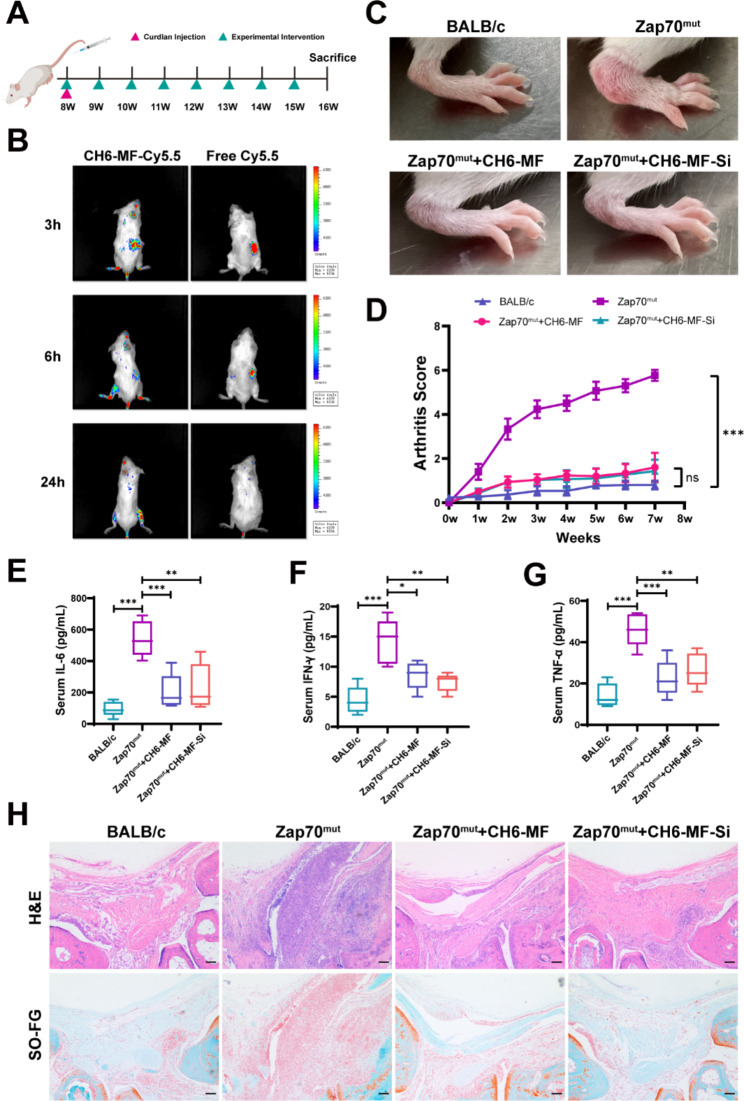
Fig. 5.
Therapeutic effect of CH6-MF NPs and CH6-MF-Si NPs in vivo. (A) The process used to test therapeutic effects in the in vivo model is shown in the schematic diagram. (B) In vivo imaging of CH6-MF-Cy5.5 and free Cy5.5 in Zap70mut mice at different times. (C) Photographs of the hind paws of BALB/c or Zap70mut mice treated with CH6-MF NPs or CH6-MF-Si NPs. (D) Inflamed joints in BALB/c or Zap70mut mice treated with CH6-MF NPs or CH6-MF-Si NPs. The mice were evaluated with clinical scores. Average levels of inflammatory cytokines, including (E) interleukin-6 (IL-6), (F) interferon-γ (IFN-γ) and (G) tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) were detected by ELISA. (H) Haematoxylin-eosin (H&E) and safranin-O (SO-FG) staining were used to assess inflammatory infiltration of the ankle joint. One-way ANOVA was performed on the data. The outcomes are presented as the mean ± SD. ns = statistically nonsignificant, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001. Scale bar = 100 μm