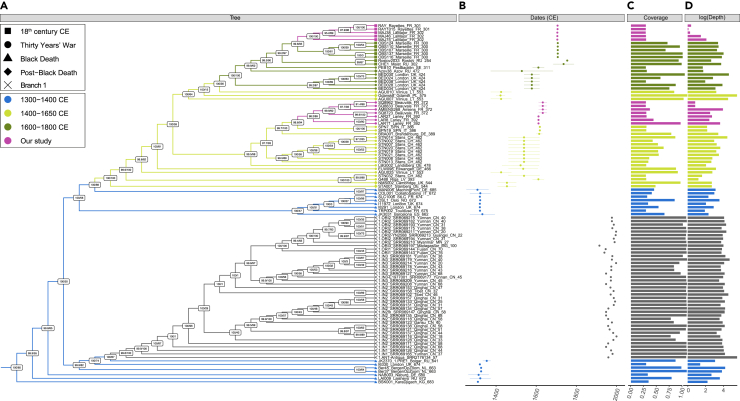
Figure 5.
Phylogenetic reconstruction
(A) Maximum Likelihood tree (IQ-TREE), considering 29,609 genome-wide variant positions known to provide reliable phylogenetic signal. This analysis included 185 previously published genomes, but the tree shown is restricted to second and third pandemic genomes, disregarding branch lengths, for clarity (the tree with branch length is shown in Figure S5). Node supports are estimated from SH-aLRT calculations (left) and ultrafast bootstrap approximation (right).
(B) Sample dates CE, with error margins representing the lower and upper boundaries provided by archaeological contexts.
(C and D) represent the coverage and the logarithm of the average sequencing depth-of-coverage achieved for the different CO92 genomes considered. The colors illustrated follow the coloring scheme from Spyrou et al., 2022,43 and the tip shapes indicate the historical context of archaeological samples investigated with respect to Figure 1. See also Figures S5 and S6.