Figure 10.
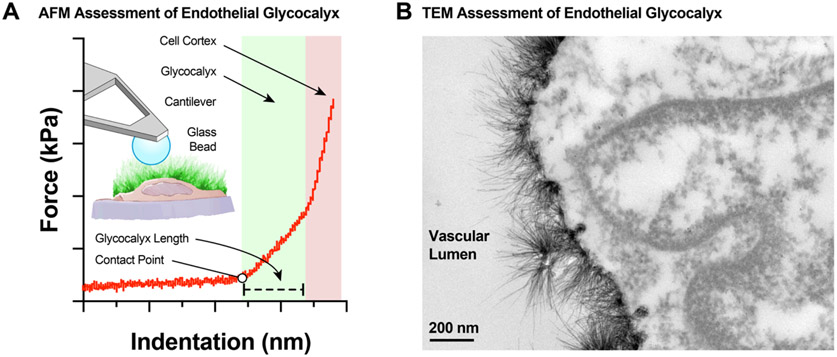
The endothelial glycocalyx is very fragile and difficult to measure. Today two commonly used techniques that provide ex vivo direct measurements of the in situ endothelial glycocalyx characteristics include atomic force microscopy (AFM) and transmitted electron microscopy (TEM). A, AFM allows for the measurement of glycocalyx length and stiffness as assessed by the force curves generated when an AFM cantilever approaches and deforms the glycocalyx structures of en face isolated vascular preparations or cultured endothelial cells. B, TEM allows for visualization of endothelial glycocalyx structures at the highest resolution currently available in microscopy, albeit, requiring complex sample preparation (Bar = 200 nm).