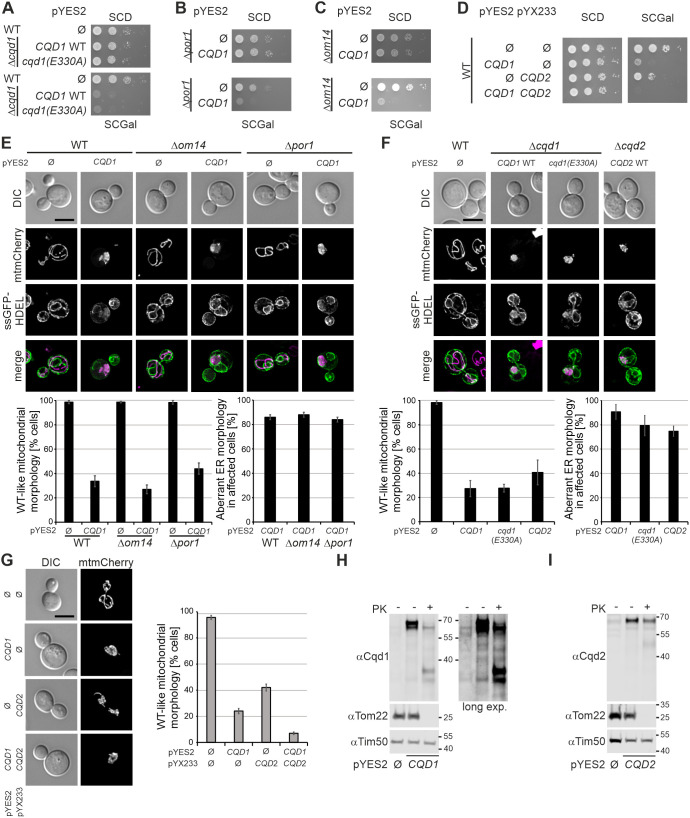
Fig. 8.
The CQD1 and CQD2 overexpression phenotypes might be a result of altered topology. (A) Overexpression of the nonfunctional cqd1(E330A) allele is toxic. Wild-type cells carrying an empty pYES2 plasmid (Ø) and Δcqd1 cells carrying pYES2 plasmids to overexpress CQD1 WT or cqd1(E330A) were grown in SCD and shifted to SCGal prior to analysis. Growth was analyzed by drop dilution assay on SCD and SCGal. (B,C) Om14 and Por1 are not required for the growth defect caused by CQD1 overexpression. Cells of the indicated strains expressing CQD1 at wild-type level or overexpressing CQD1 were analyzed as in A. (B) Analysis of the CQD1 overexpression phenotype in the Δpor1 background. (C) Analysis of the CQD1 overexpression phenotype in the Δom14 background. (D) Simultaneous overexpression of CQD1 and CQD2 is almost lethal. Growth of wild-type cells carrying the indicated pYES2 and pYX233 plasmids to overexpress CQD1 and/or CQD2 was analyzed as in A. (E) Overexpression of CQD1 results in the formation of mitochondria–ER clusters in absence of Om14 and Por1. The indicated strains expressing mtmCherry and ssGFP-HDEL were grown to logarithmic growth phase in SCGal, fixed with formaldehyde, and examined by deconvolution fluorescence microscopy. Upper panel, maximum intensity projections of z stacks of entire cells (mitochondria) or of the center of the cells (ER, five consecutive z sections). DIC, differential interference contrast. Scale bar: 5 μm. Lower panel, quantitative evaluation of mitochondrial and ER morphologies. Columns represent mean±s.d. values from three independent experiments. In each experiment, mitochondrial morphology of at least 100 cells per strain was quantified. For the overexpression strains, also ER morphology of at least 50 cells with altered mitochondrial morphology was analyzed. (F) Overexpression of cqd1(E330A) and CQD2 also leads to the generation of mitochondria–ER clusters. The indicated strains were analyzed as in E. (G) Simultaneous overexpression of CQD1 and CQD2 exacerbates the mitochondrial morphology defect phenotype. Mitochondrial morphology of the indicated strains expressing mtmCherry was analyzed as in E. (H) Overexpression of CQD1 leads to an altered topology. Intact mitochondria from cells expressing CQD1 at wild-type level or overexpressing CQD1 were left untreated or were treated with proteinase K (PK). The indicated fractions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting. Two different exposures of the anti-Cqd1 decoration are shown to better visualize Cqd1 at wild-type level. (I) Overexpression of CQD2 leads to an altered topology as well. Intact mitochondria from cells expressing CQD2 at wild-type level or overexpressing CQD2 were treated as in (H). Images in A–D, H and I are representative of at least three repeats.