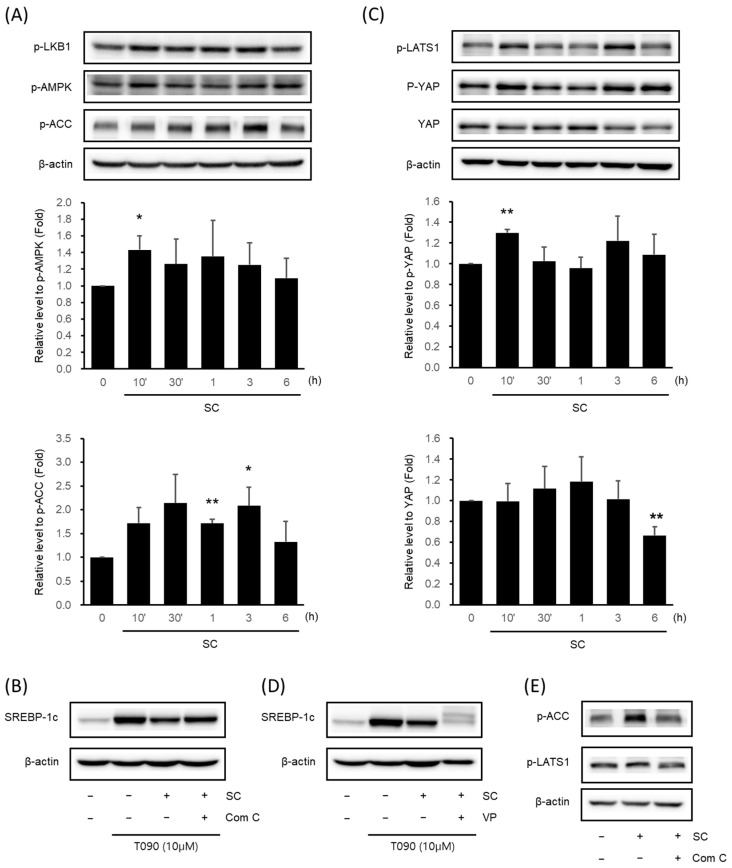
Figure 3.
Effect of SC on activation of AMPK signaling pathway and Hippo-YAP signaling pathway. Immunoblotting analysis of key proteins in the AMPK pathway (A) and Hippo-YAP pathway (C). HepG2 cells were cultured in serum-free media for 12 h, followed by treatment with 100 μg/mL of SC for the indicated time period. Key proteins in each pathway, p-AMPK, p-ACC, p-YAP, and YAP, were tested in at least three replicates. Results were expressed as the mean ± SD, and statistical significance was indicated as * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 when comparing control and SC-treated cells. (B) Differences in SREBP-1c expression by Compound C: an AMPK inhibitor. HepG2 cells were treated with 10 μM Compound C for 30 min prior to treatment with 100 μg/mL SC for 1 h, followed by treatment with T090 (10 μM) for 12 h. (D) Changes in SREBP-1c expression by the YAP inhibitor, VP. HepG2 cells were treated with 0.6 μM VP for 30 min prior to treatment with 100 μg/mL SC for 1 h, followed by treatment with T090 (10 μM) for 12 h. (E) Expression of p-LATS1, a key protein in the Hippo-YAP pathway, by AMPK inhibition. HepG2 cells were treated with 10 μM Compound C for 30 min, followed by treatment with 100 μg/mL SC for 30 min.