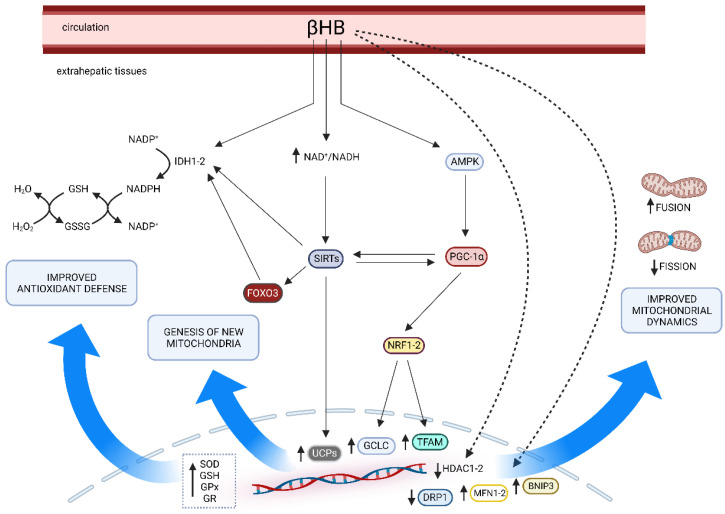
Figure 1.
The main pathways involved in the multiple effects of KD on mitochondrial health. The blue arrows suggest the main effects driven by βHB-influenced factors (i.e., improved antioxidant defense, genesis of new mitochondria, and improved mitochondrial dynamics). AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; BNIP3, Bcl-2 interacting protein 3; DRP, dynamin related protein 1; GCLC, glutamate cysteine ligase catalytic subunit; GPx, glutathione peroxidase; GR, glutathione reductase; HDAC1-2, histone deacetylases 1-2; IDH1-2, isocitrate dehydrogenase 1-2; MFN2, mitofusin 2; NAD, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; NADP, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; NRF1-2, nuclear respiratory factors 1-2; PGC1-α, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator 1α; SIRTs, sirtuins; SOD, superoxide dismutase; TFAM, mitochondrial transcription factor A; UCPs, mitochondrial uncoupling proteins. Created with BioRender.com, accessed on 25 April 2023.