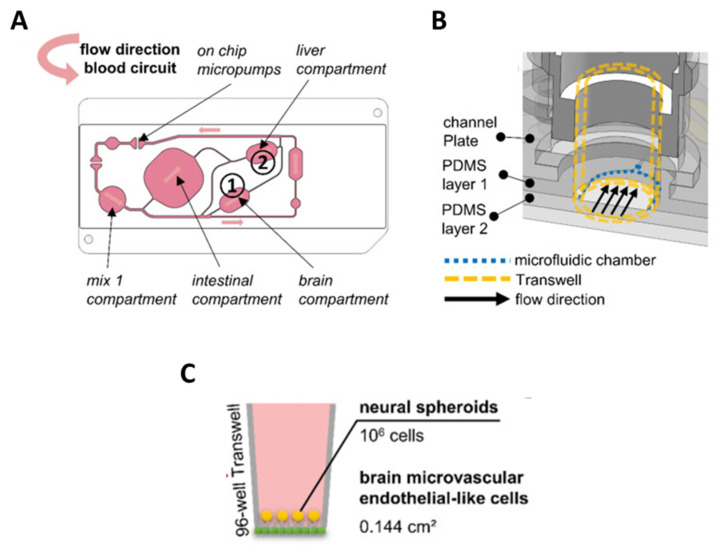
Figure 6.
Multi-organ microfluidic system developed by Koenig et al. [93]. (A) 2D view of the microfluidic chip; the surrogate blood circuit is shown in pink. In the depicted circuit, a medium reservoir (mix 1) is interconnected with a 24-well intestinal compartment and 96-well compartments for the liver ① and BBB/brain ② model. The fluid flow is created by on-chip micropumps, and the direction of the flow is indicated by arrows. (B) 3D view of the brain culture compartment. The bottom of the compartment consists of the PDMS layer 2. At the sides, the compartment consists of the PDMS layer 1 and the channel plate. Cut-off 96-well Transwells (yellow dotted line) can be inserted into the compartment and stand at their edges on a 100 µm-high step of PDMS layer 2. Endothelial cells cultured at the bottom of the Transwell membrane are thereby directly exposed to the fluid flow passing underneath. (C) Schematic representation of the brain microvascular endothelial-like cells and neural spheroids were combined in 96-well Transwells to build a blood–brain-barrier/brain model. OA publishing license: Adapted from Koenig et al. [93].