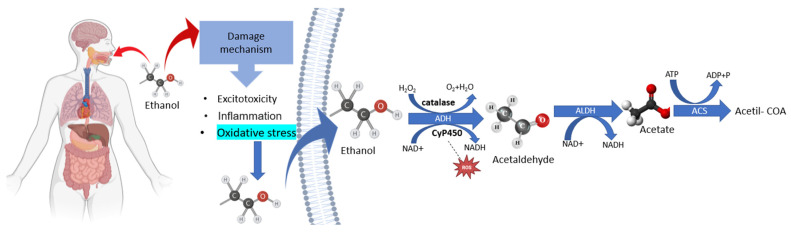
Figure 1.
Representative schematic of the toxic damaging mechanisms of ethanol (cytotoxicity, inflammation, and oxidative stress) and its hepatic metabolization in the human body. The enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) oxidizes ethanol to acetaldehyde. This, in turn, undergoes the action of aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH), generating the acetate molecule that participates in several metabolic cycles.