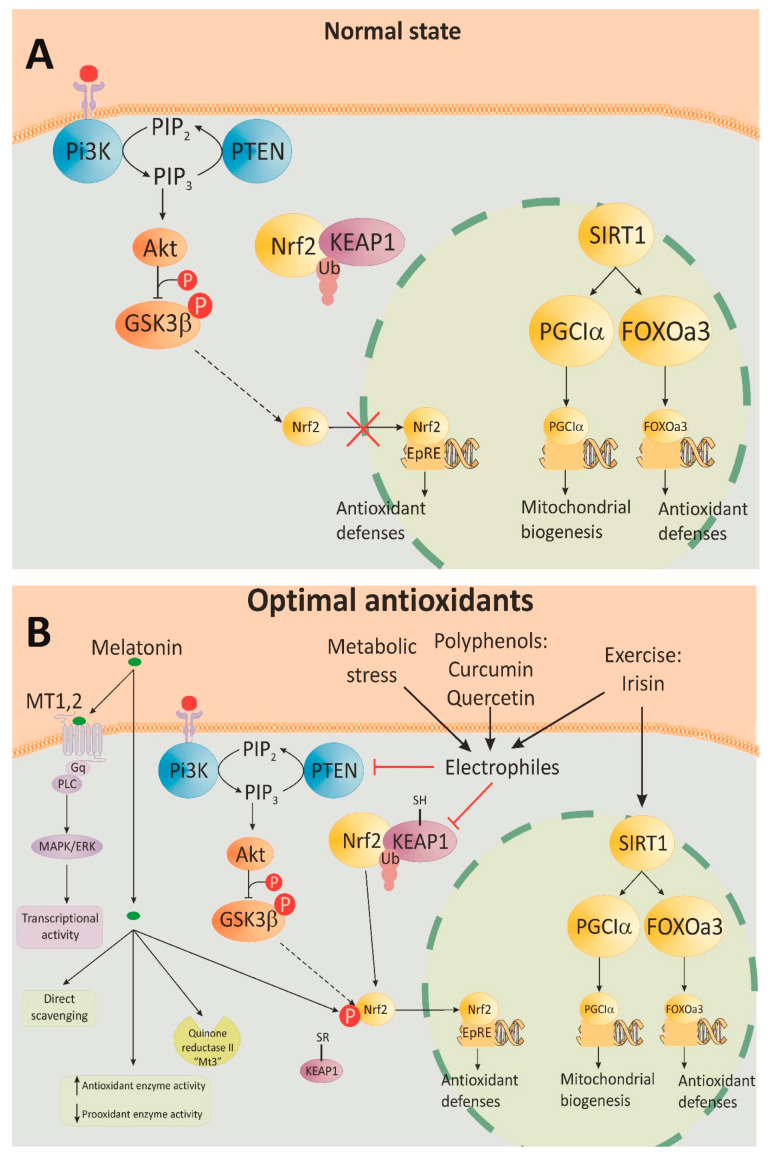
Figure 1.
Nrf2 and SIRT1 signaling pathways regulation by antioxidants. (A) At optimal conditions, Nrf2 forms a KEAP1-ubiquitin complex, which downregulates Nrf2 via proteasomal degradation. Nrf2 activity is also inhibited by PTEN. This phosphatase decreases 3-phosphoinositides (PIP3) by conversion into PIP2, and the downstream Akt-GSK3β are not activated. The small amount of Nrf2 cannot be phosphorylated and translocated into the nucleus. Another mechanism of antioxidants involves SIRT1/FOXOa3 and the PGC1α pathway by expression of the antioxidant defense genes and mitochondrial biogenesis. (B) With physiological doses of antioxidants, KEAP1 is oxidized and the Nrf2 complex is destroyed, which results in an increased amount of Nrf2. PTEN is also suppressed and, thus, activates the previously described pathway with the following translocation of Nrf2 into the nucleus. Phosphorylated Nrf2 binds to the electrophile response element (EpRE) that starts the expression of the phase II antioxidant enzymes. Metabolic stress activates the Nrf2 pathway in the same manner. Moderate physical exercise stimulates both Nrf2 and SIRT1 signaling. Melatonin exerts its antioxidant effects through receptor-mediated transcriptional activity and after diffusion in the cytosol via several different pathways.