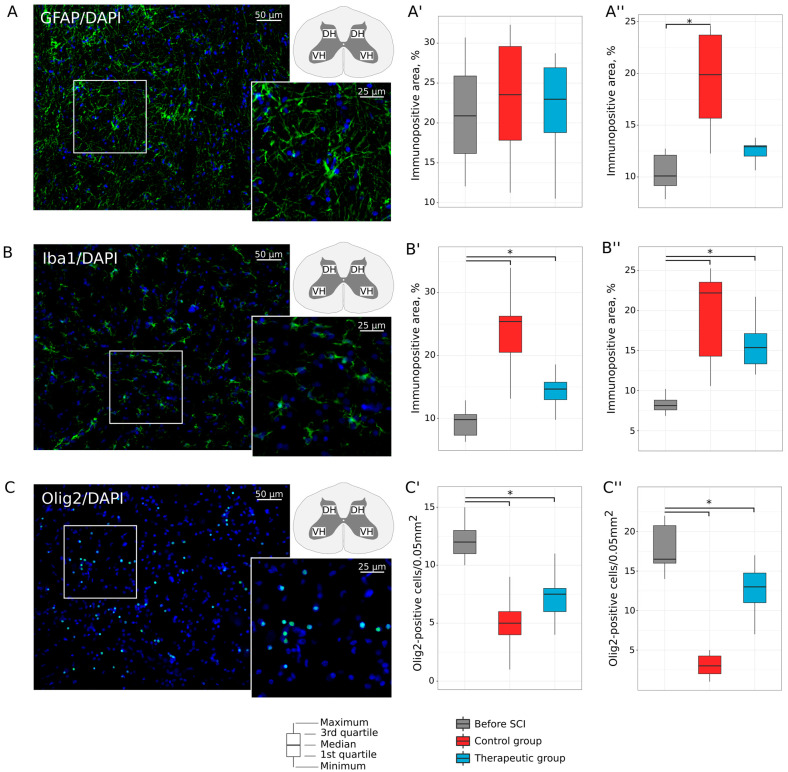
Figure 5.
Immunofluorescence staining of the ventral and dorsal horns of the lumbar spinal cord in mini pigs 8 weeks after low thoracic spinal cord injury (SCI). (A) Immunopositive reaction with an antibody against a glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) (green glow) in an intact animal. (A′,A″) Morphometric analysis demonstrates relative GFAP-positive area in the ventral and dorsal horns, correspondingly, in the experimental groups. (B) Immunopositive reaction with an antibody against an ionized calcium binding adaptor molecule 1 (Iba1) (green glow) in an intact animal. (B′,B″) Morphometric analysis demonstrates relative Iba1-positive area in the ventral and dorsal horns, correspondingly, in the experimental groups. (C) Immunopositive reaction with an antibody against an oligodendrocyte transcription factor (Olig2) (green glow) in an intact animal. (C′,C″) Morphometric analysis demonstrates the number of Olig2-positive nuclei in the ventral and dorsal horns, correspondingly, in the experimental groups. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue glow). Inserts demonstrate the zooming part of images. The squares inserted in the schematic transverse spinal cord indicate the areas used for immunofluorescence analysis, VH—ventral horn and DH—dorsal horn. Data are visualized using box plots, *—p < 0.05.