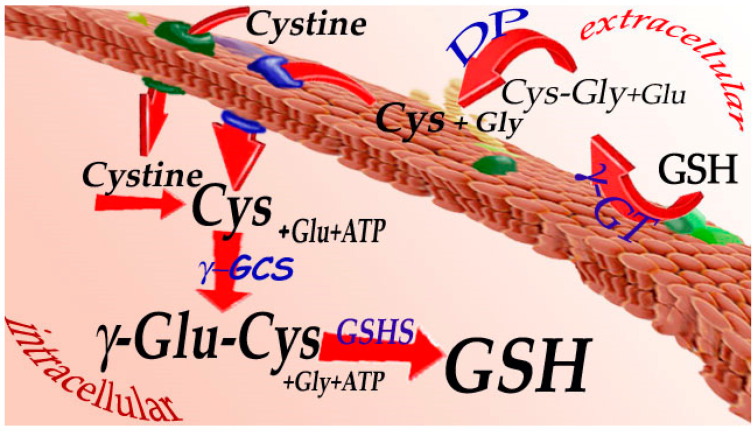
Figure 3.
GSH synthesis and degradation. GSH is synthesized by a two-step enzymatic reaction involving γ-glutamylcysteine syntethase (γ-GCS) and GSH synthetases (GSHS) in sequence. γ-GCS catalyzes the formation of the dipeptide γ-glutamylcysteine (γ-Glu-Cys), and GSHS catalyzes the binding of glycine to γ-Glu-Cys to form GSH. This reaction occurs in the cytoplasm of each cell. Cysteine (Cys), which is the rate-limiting factor for this synthesis, can also be obtained by reduction of cystine once it enters the cells. GSH is enzymatically degraded to cysteinylglycine (Cys-Gly) by γ-glutamyltranspeptidase (γ-GT), which is located on the outer surface of plasma membranes. Cys-Gly can then be hydrolyzed into the individual amino acids by extracellular dipeptidases (DP). Glu, glutamic acid; Gly, glycine.