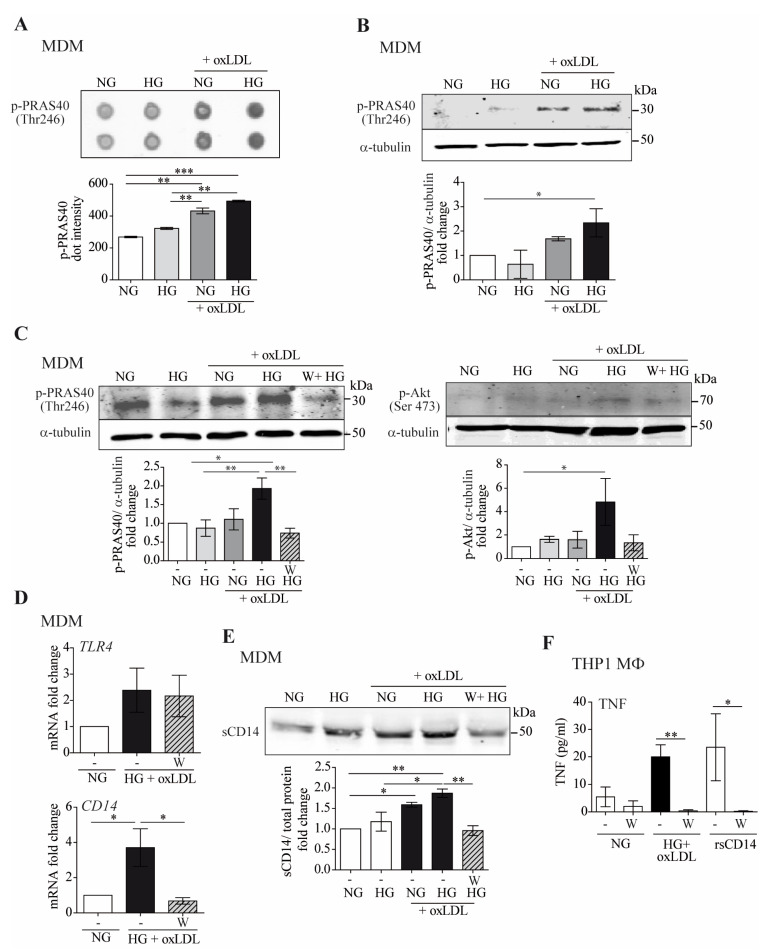
Figure 5.
The combination of high glucose and oxLDL promotes sCD14 shedding though Akt-PRAS40 pathway activation. MDM were treated with 150 μg/mL of oxLDL for 24 h in culture medium containing 5 mM (normal glucose, NG) or 15 mM (high glucose, HG) of glucose. (A) MDM lysates were exposed to phospho-kinase array spotted membranes. Upper panel: dot images. Lower graph: quantification of dot intensities. (B) Cell lysates were probed with anti-pPRAS40 (Thr246) by Western blotting, and equal loading was determined by probing with α-tubulin. Upper panel: representative Western blot images, lower panel: mean ± SEM fold induction levels relative to untreated MDMs (NG) from 2 independent donors. (C–F) Cells were incubated for 45 min with 10 µM of wortmannin (W) for 24 h prior to oxLDL stimulation under NG or HG conditions. (C) PRAS40 (Thr246) and Akt (Ser473) phosphorylation determined by Western blotting. Upper panel: representative images. Lower panel: graph showing fold induction levels relative to untreated cells (NG) from 4 donors. (D) TLR4 and CD14 mRNA expression analyzed by RT-PCR. The data show the mean fold change relative to untreated cells (NG) ± SEM from 4 donors. (E) sCD14 in culture supernatants measured by Western blotting. Upper panel: representative Western blot images. Lower panel: band intensity values/total protein. Fold induction levels relative to untreated cells (NG) from 4 donors are shown. (F) THP1 MΦ were pre-incubated with wortmannin (W) and then treated with NG, HG + oxLDL, and with 2 µg/mL of rsCD14. After 24 h, TNF in culture supernatants was measured by ELISA. Graph showing the mean ± SEM from 3 independent experiments performed in triplicate (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, Mann–Whitney test). MDM: monocyte-derived macrophages.