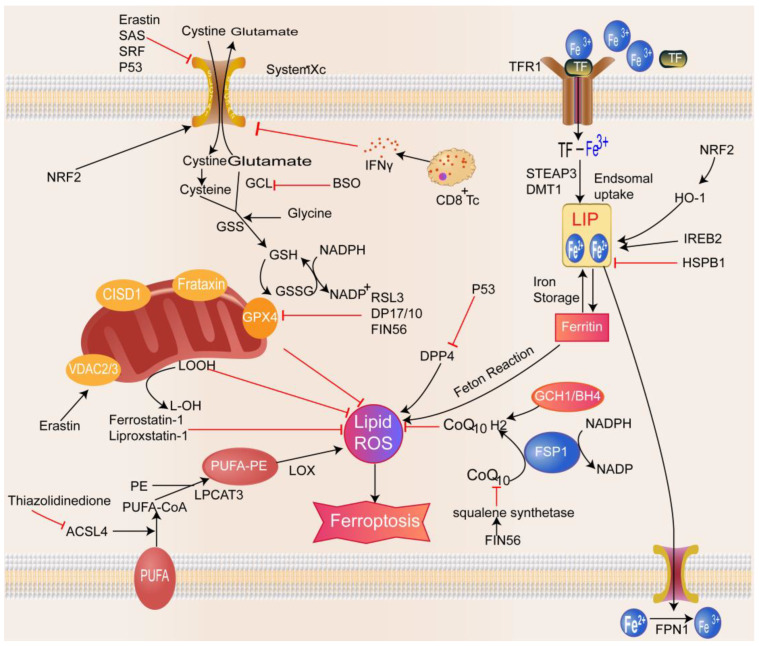
Figure 1.
Mechanisms of ferroptosis. Ferroptosis is mainly related to disorders of amino acid metabolism, accumulation of lipid peroxides, and disorders of iron ion metabolism. Xc complex imports cystine for the synthesis of glutathione. GPX4 uses glutathione to prevent the accumulation of lipid-reactive oxygen species. The classical Fenton reaction between Fe3+ and Fe2+ produces abundant reactive oxygen species. Decreased iron stores or increased iron intake can lead to iron overload and eventually iron death. In addition, other signaling pathways and regulators control ferroptosis sensitivity. For example, erastin can bind to porin 2/3 on the outer mitochondrial membrane, causing mitochondrial dysfunction and the release of many oxidative substances, ultimately leading to ferroptosis.