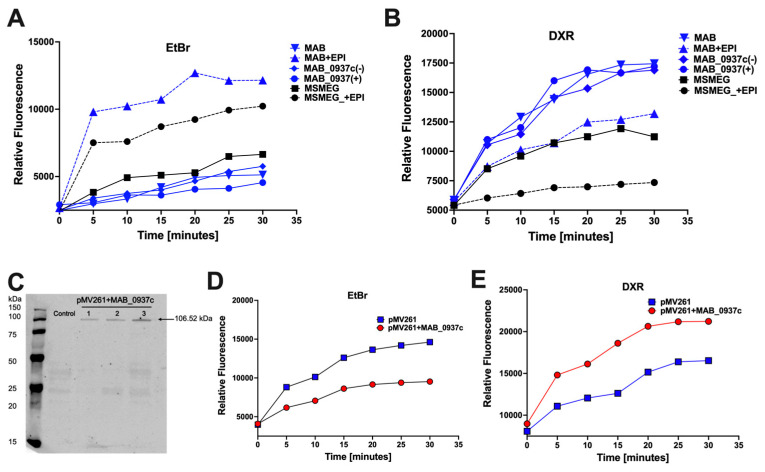
Figure 8.
Measuring the MAB_0937c efflux activity. (A) The EtBr accumulation assay in M. smegmatis (MSMEG) and the wild-type, knockout, and complemented clones of MAB in the presence or absence of EPIs. (B) The DXR efflux assay in M. smegmatis and the wild-type, knockout, and complemented clones of MAB in the presence or absence of EPIs. For better visualization, MAB groups are marked in blue and MSMEG groups in black. (C) The Western bolt analysis of His-tagged MAB_0937c protein in M. smegmatis clones. The MAB_0937c protein overexpression clone was constructed using the pMV261:His vector. Three KM50-resistant M. smegmatis clones alongside control that contained the empty plasmid were mechanically disturbed using a bead beater. The cleared samples were run on 12.5% SDS–PAGE gel, and proteins on a nitrocellulose membrane were visualized on the Odyssey Imager (Li-Cor) using the His-tag primary antibody and a corresponding IRDye secondary antibody. (D) The EtBr accumulation assay was performed for the MAB_0937c overexpression M. smegmatis clone (in red) and the control clone carrying empty pMV261 plasmid (in blue). (E) The DXR efflux assay was carried out in the MAB_0937c overexpression M. smegmatis clone (in red) in comparison with the control clone (in blue). The accumulation/efflux dynamics were measured at 37 °C and in the presence of glucose, and readings were recorded every five-minute interval up to 30 min using the Tecan fluorometer (excitation/emission 530/590 nm for EtBr and 460/590 nm for DXR). The data represent means of eight technical replicates.