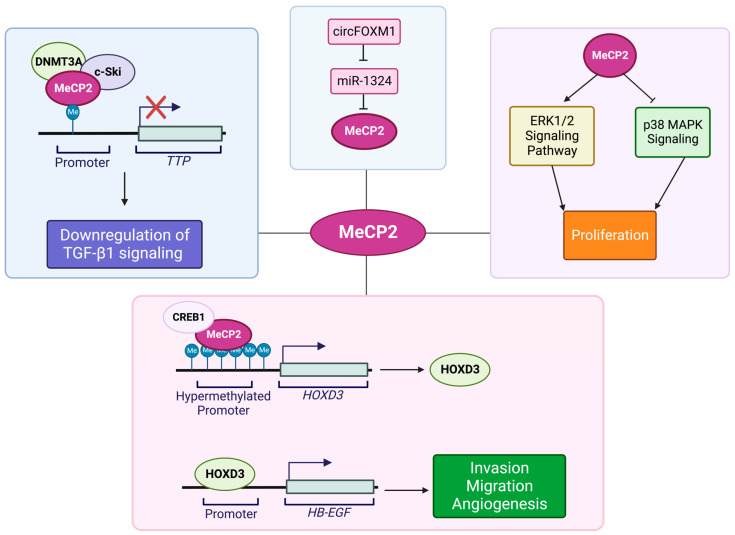
Figure 5.
Schematic representing the suspected roles of and molecular pathways involving MeCP2 in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Hypermethylation of the TTP promoter, and subsequent repression of TTP expression, is involved in the downregulation of TGF-β1 signaling in the progression of HCC via the recruitment of HDAC complexes by MeCP2 [126]. Activation of the ERK1/2 signaling pathway and inhibition of p38 activity by MeCP2 promotes cell proliferation in HCC [127]. Binding of MeCP2 and CREB1 to the hypermethylated HOXD3 promoter increases the expression of HOXD3. Binding of HOXD3 to the HB-EGF promoter results in increased HB-EGF activation and increased cell invasion and migration of HCC cells [129]. Negative regulation of MeCP2 in sorafenib resistance by miR-1324 is alleviated in the presence of circFOXM1, leading to increased expression levels of MeCP2 [130]. Illustration is generated using BioRender.com.