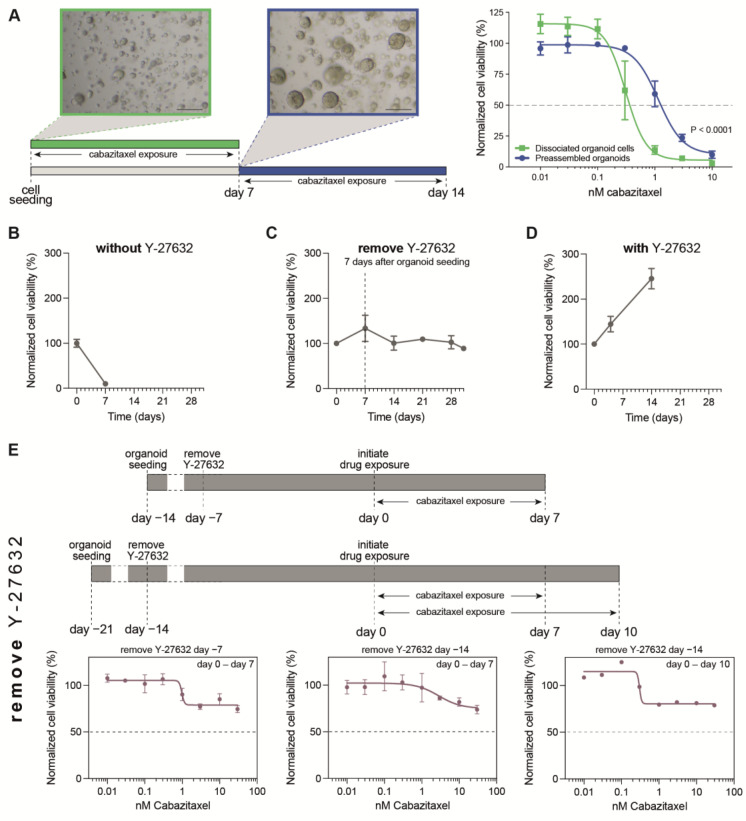
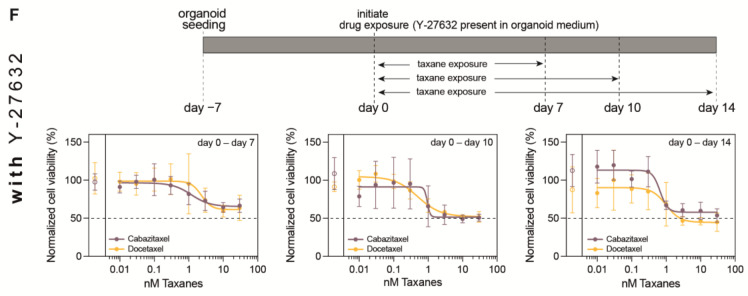
Figure 1.
Optimization of PDXO drug testing conditions. (A) Impact of organoid formation prior to drug testing. Schematic representation of experimental design as applied in Van Hemelryk et al. [21]: drug exposure was initiated immediately after cell seeding, on dissociated organoid cells (green), or after 7 days, when organoids were formed (preassembled organoids, blue). Scale bar represents 100 μm. Cabazitaxel-exposed MSK-PCa1 organoids are shown as an example. Dose–response curves depict mean +/− SEM of four independent experiments with three technical replicates per dose, with viability normalized to ethanol controls. Data curated from [21]. (B–D) Impact of Y-27632 on organoid proliferation. Viability of PC2416-DEC PDXOs starting from the day of seeding, (B) without Y-27632 present in organoid culture medium, (C) with Y-27632 removed after 7 days, and (D) with Y-27632 continuously present in organoid culture medium. (E) Impact of organoid viability on treatment efficacy in correspondence with (C). Y-27632 was removed from culture medium 7 days after organoid seeding and from 7 to 14 days prior to drug exposure, as indicated on the timelines. PC2416-DEC PDXOs were exposed to cabazitaxel for 7 days (left and middle panel; mean +/− SEM of two independent experiments with six technical replicates per dose) or for 10 days (right panel; mean of six technical replicates per dose). Normalization to vehicle (ethanol) controls. (F) Impact of drug exposure time on treatment efficacy in correspondence with (D). In the presence of Y-27632, PC2416-DEC PDXOs were exposed to docetaxel or cabazitaxel for 7, 10 or 14 days (mean +/− SD of six technical replicates per condition). Normalization to vehicle (ethanol) controls of both treatment plates. Open dots represent vehicle controls of each treatment plate.