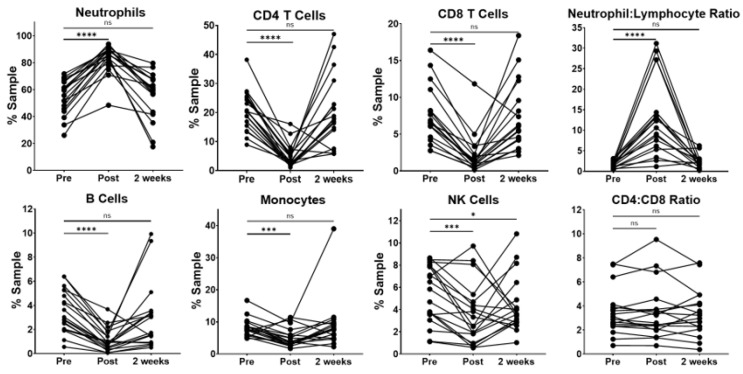
Figure 1.
Lung resection results in the transient increase in neutrophils, but a stable CD4–CD8 ratio. Matched dot plots of each cell type, the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and CD4-to-CD8 ratio at three time points, from prior to surgery (Pre, n = 19), immediately following surgery (Post, n = 19) and 2 weeks after surgery (2 weeks, n = 18). Dots connected by lines indicate individual patients. There is a statistically significant increase in the percentage of neutrophils immediately following surgery and a corresponding decrease in all other cells types. These frequencies return to baseline for all cell types 2 weeks after surgery, except for a slight continued decrease in NK cells (mean 5.4% vs. 4.4%, p < 0.05). There is a transient, variable increase in the NLR in patients immediately after surgery, with no significant change by 2 weeks. The CD4–CD8 T cell ratio remained relatively stable in patients across the three time points. Significance determined via paired Student’s t tests. ns: non-significant, * p < 0.05, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001.