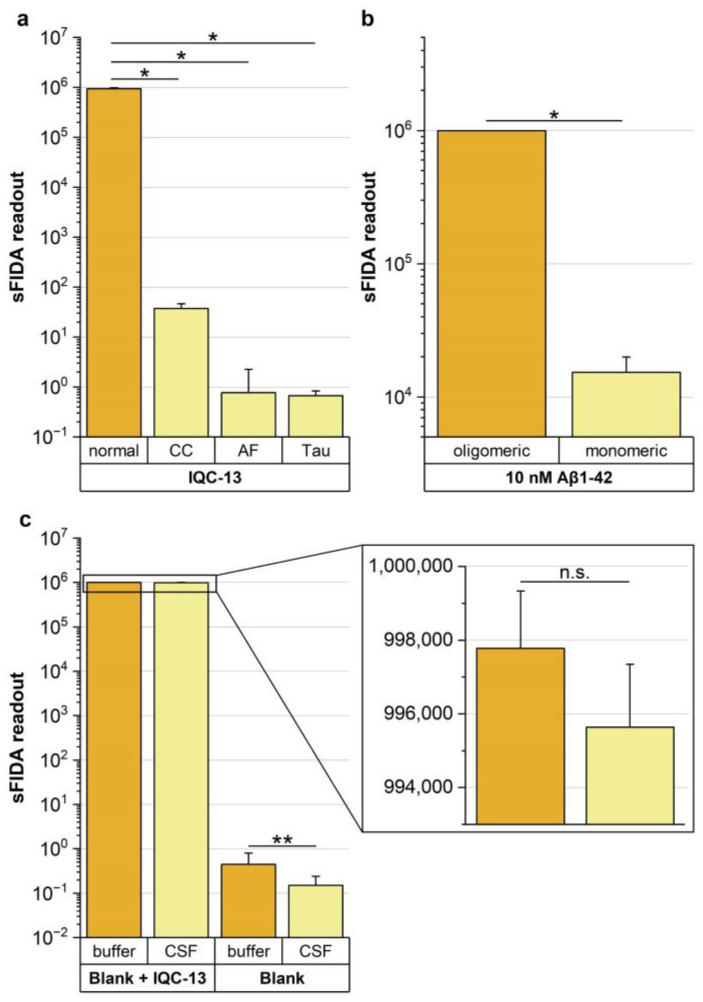
Figure 4.
Comparison of sFIDA readout of IQC-13 applied on different assay setups. (a) sFIDA readouts of the normal assay setup were compared to assay setups without the capture antibody (capture control, CC), without Aβ-specific detection probes (TBST + 0.1% BSA without any detection probes, autofluorescence control, AF) or with Tau-specific detection probes (equimolar mixture of Tau12 antibodies labeled with CF633 and CF488A in TBST + 0.1% BSA, Tau). A signal reduction of almost 100% and significantly lower sFIDA readouts compared to the standard assay setup (normal, p-values between 0.0152 and 0.0147) were observed for all controls. (b) In addition, equal molar concentrations of monomeric Aβ1–42 were applied on the assay surface to demonstrate that the assay is insensitive toward monomers. A signal reduction of nearly 99% and significantly lower sFIDA readouts compared to the standard assay setup were observed (p-value: 0.0152), showing that interference from monomeric Aβ can be excluded. (c) To evaluate the matrix effects of CSF, IQC-13 was spiked into bovine CSF, and sFIDA readouts were calculated on the basis of the background signal of the additionally applied bovine CSF-blank. For IQC-13, no significant difference in the sFIDA readouts was observed (p-value: 0.108), and only a slight signal reduction of 0.2% was observed. In contrast, the sFIDA readout of CSF-blank was significantly lower compared to the buffer control (p-value: 0.002, signal reduction: 67%). Note the logarithmic scale. Data are presented as the mean and standard deviation of four replicates. Significant differences between groups were calculated using the one-sided Mann–Whitney U test with a confidence interval of 5%. Significant differences are marked as follows: * 0.01 ≤ p < 0.05; ** 0.001 ≤ p < 0.01; n.s. not significant. Abbreviations: CSF, cerebrospinal fluid; IQC, internal quality control.