Figure 1.
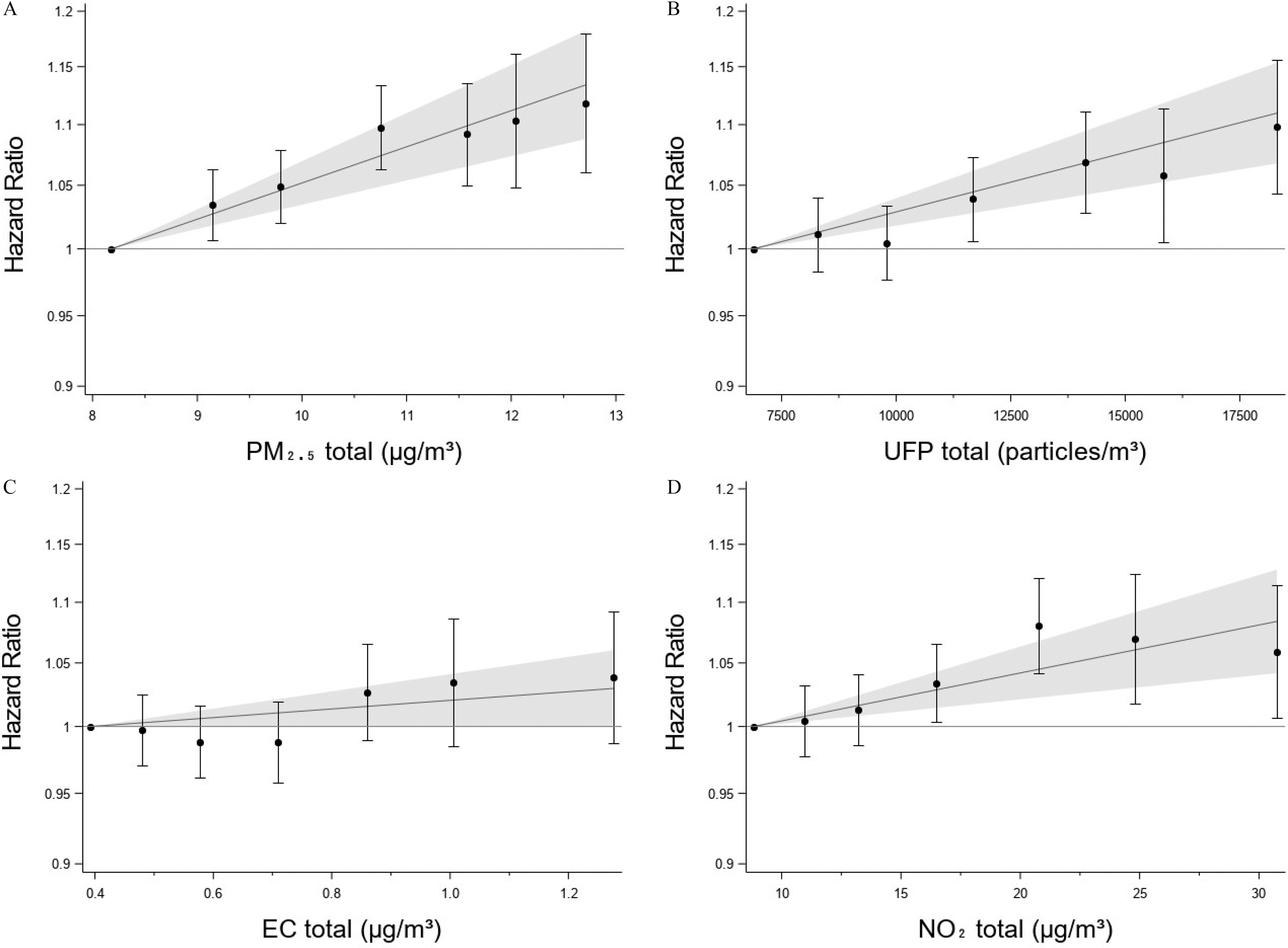
Associations between MI and 5-y time-weighted averages of (A) , (B) UFP, (C) EC, and (D) specified both in categories and as linear variables in the fully adjusted model 3. Categories defined from percentile of exposure: (reference), 10%–25%, 25%–50%, 50%–75%, 75%–90%, 90%–95%, and ; HRs and 95% CI plotted at the median of each category. The linear estimates from Table 2 with 95% CIs are plotted with the median of the categorical reference category as the null (). (Table S3 holds the same information in tabulated form). Denmark, 2005–2017, . Note: CI, confidence interval; EC, elemental carbon; MI, myocardial infarction; UFP, ultrafine particles.
